# Snapchain
## Getting Started
:::tip
If your goal is to get started as quickly as possible, consider a managed service like [Neynar](https://neynar.com/) instead of running your own node.
:::
### Requirements
* 16 GB of RAM
* 4 CPU cores or vCPUs
* 2 TB of free storage
* A public IP address with ports 3381 - 3383 exposed
### Sync a node
The easiest way to run Snapchain is using [Docker](https://www.docker.com/get-started/). Once installed, run the following commands in a new folder
```bash
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/farcasterxyz/snapchain/refs/heads/main/scripts/snapchain-bootstrap.sh | bash
```
Check the the docker logs to ensure that the snapshot is being downloaded.
```bash
./snapchain.sh logs
2025-04-16T02:40:11.265909Z INFO snapchain: Downloading snapshots
2025-04-16T02:40:11.266021Z INFO snapchain::storage::db::snapshot: Retrieving metadata from https://pub-d352dd8819104a778e20d08888c5a661.r2.dev/FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET/1/latest.json
2025-04-16T02:40:11.637368Z INFO snapchain::storage::db::snapshot: Downloading zipped snapshot chunk chunk_0001.bin
2025-04-16T02:40:12.952768Z INFO snapchain::storage::db::snapshot: Downloading zipped snapshot chunk chunk_0002.bin
2025-04-16T02:40:15.305951Z INFO snapchain::storage::db::snapshot: Downloading zipped snapshot chunk chunk_0003.bin
2025-04-16T02:40:17.742041Z INFO snapchain::storage::db::snapshot: Downloading zipped snapshot chunk chunk_0004.bin
2025-04-16T02:40:20.720477Z INFO snapchain::storage::db::snapshot: Downloading zipped snapshot chunk chunk_0005.bin
....
```
Snapshots are about 200 GB in size and may take a few hours to sync and decompress. Once complete, you should see logs like this:
```
2025-04-16T08:20:01.749980Z INFO node{name=Block}:sync{height.tip=[0] 1875918 height.sync=[0] 1875919}: informalsystems_malachitebft_sync::handle: Requesting sync value from peer height.sync=[0] 1875920 peer=12D3KooWCc28TYrrXFivwUshyZ8R5HqPMgx4f7AP54iCDLYr7kFR
2025-04-16T08:20:01.752425Z INFO Actor{id="0.7"}: snapchain::consensus::read_validator: Processed decided block height=[0] 1875920 hash="d7a6e107fed6e1e90d4888f4aa2bfb922d9e6950d83c621db0500b15e1caccfe"
```
It will take a few hours for the node to sync. You can monitor it by running:
```bash
curl localhost:3381/v1/info | jq
# if the nodes are in sync, the blockdelay values for shards should be in the single digits.
{
"dbStats": {
"numMessages": 656823920,
"numFidRegistrations": 1049519,
"approxSize": 324437755099
},
"numShards": 2,
"shardInfos": [
{
"shardId": 0,
"maxHeight": 1932723,
"numMessages": 0,
"numFidRegistrations": 0,
"approxSize": 1114006028,
"blockDelay": 5,
"mempoolSize": 0
},
{
"shardId": 2,
"maxHeight": 1945363,
"numMessages": 326936052,
"numFidRegistrations": 523905,
"approxSize": 161319650355,
"blockDelay": 6,
"mempoolSize": 4294967295
},
{
"shardId": 1,
"maxHeight": 1966901,
"numMessages": 329887868,
"numFidRegistrations": 525614,
"approxSize": 163118104744,
"blockDelay": 5,
"mempoolSize": 4294967295
}
]
}
```
### Query a node
Once the node is in sync you can start querying it for the latest messages from a user. You'll need the user's account id to get their messages. If you don't have this handy, you can do a lookup by username from the public Farcaster name server.
```bash
# Query for the id associated with the @farcaster account
curl https://fnames.farcaster.xyz/transfers?name=farcaster
{
"transfers": [
{
"id": 1,
"timestamp": 1628882891,
"username": "farcaster",
"owner": "0x877...06ed",
"from": 0,
"to": 1,
"user_signature": "0xa6fdd...471b",
"server_signature": "0xb718...c41b"
}
]
}
```
The `@farcaster` user's account id is 1, and so you can fetch the latest messages by querying the node over its [HTTP API](/reference/httpapi/httpapi):
```
curl http://localhost:3381/v1/castsByFid\?fid\=1 \
| jq ".messages[].data.castAddBody.text \
| select( . != null)"
```
## Whitepaper
### Abstract
Snapchain is a blockchain-like network for storing and syncing Farcaster's social data. It has stronger and faster consistency guarantees than the current [deltagraph](https://www.varunsrinivasan.com/2024/04/28/the-goldilocks-consensus-problem) system which is finding it hard to keep all the nodes in sync in near real-time. The tradeoff we make for the consistency improvements is a new consensus step that introduces more complexity and failure modes which must be addressed.
### Problem
A decentralized social network is one where two users can find each other and communicate, even under adverse conditions. Users must be able to run a node and use it to communicate with each other. Each node must reach consensus about a user’s state and stay in sync with other nodes. If Alice follows Bob at one node, it must make sure that she wasn’t already following Bob and then update this relationship on every other node.
Users generate a lot of transactions and expect real-time delivery. Twitter, for example, has 200M daily users and sees 10k TPS and is
likely to see 1TB - 10TB/day in state growth. Existing decentralized networks can’t handle this kind of load with real-time delivery. It’s not because it’s impossible, but because they make tradeoffs to solve different user problems. Blockchains move money and are designed to prevent double spends, which makes sharding and pruning data difficult. Federated systems like email are shard-able but have weak decentralization and consistency, which makes apps harder to build. See Appendix D for more details.
Farcaster has used a CRDT-based system called a [deltagraph](https://www.varunsrinivasan.com/2024/04/28/the-goldilocks-consensus-problem) to decentralize social data. By defining every transaction as a CRDT operation, consensus is reached immediately without coordination at the local node. The changes are then gossiped out to peers which can lazily update their own state. The network served 100k users doing 500 TPS with 2GB/day state growth in early 2024.
As the network grew to thousands of nodes, some of them get out of sync due to gossip failures. Since CRDTs are unordered, a node could only detect gossip failures by syncing manually with every other node and comparing all transactions. This becomes slow and eventually infeasible as the number of nodes and valid messages cross some threshold (see Appendix C). The lack of ordering also meant that the network cannot enforce global rate limits, and they must be localized to each node. The side effect of this is that a transaction that passes the limits on one node might be rejected by another. Without strict ordering, it's hard to guarantee both real-time delivery and strong consistency.
### Specification
Snapchain introduces transaction ordering and blockchain-like semantics to Farcaster. A block production step is added which groups and orders user transactions. Syncing is much simpler since a node only needs to find and download missing blocks. Snapchain, like the deltagraph before it, relies on an external blockchain to handle account creation and fee collection.
Snapchain is different from most blockchains because its transactions are not turing complete, are account independent and pruned often. A transaction is a "post", "like" or other social operation which only affects a single account. This is important for scaling since it prevents the network from being used for non-social purposes and makes sharding by account easy. Older transactions are pruned to clear data from inactive users or negating transactions, such as when a user likes and unlikes the something.
The initial release of snapchain should support a TPS of [> 9000](https://youtu.be/-p_SWPZ1_ew?si=peDiLXEZ1csgFGPc\&t=98) which would support 2 million daily users.
#### 1. Accounts
Users create and manage accounts using an external blockchain. This incurs some fees during setup but is necessary for the strong security and consistency guarantees. Calling the registry contract onchain issues a unique account number or *farcaster id* to the wallet. Signed messages from this wallet are treated by Snapchain as authorized actions from the account. Accounts can be transferred between wallets at any time, though an address may only own one account at a time.
Accounts can acquire human-friendly ENS usernames by proving ownership with an onchain or offchain proof. All references to the account are made to the farcaster id, which in turn is mapped to the verified ENS username by clients. This lets users change their username without having to resign all data on the network. This system can also be extended to non-ENS name systems if desired.
Accounts can issue "app keys" onchain which are keys with a narrower set of permissions. They can post messages on behalf of the account but cannot change ownership of the account or modify other app keys. They are used like auth tokens to delegate permissions to clients safely. It may be possible to implement app keys on Snapchain in future, avoiding onchain fees for modifying them.
 Account recovery is built into registry contract which lets the wallet nominate another address which also controls the farcaster id. This could be set to the user's primary wallet, an m-of-n social recovery multisig or institutional recovery wallet. User may also compose their own recovery systems by converting the wallet into a smart wallet which can implement custom recovery logic.
#### 2. Transactions
A *blockchain transaction* is a Farcaster specific transactions that happens on an external blockchain. An example is when Alice makes a transaction to the registry contract to get her farcaster id and set up her app keys. Snapchain nodes listen to and store blockchain transactions in their history.
A *snapchain transaction* is a social action like making a new post. Alice says “Hello World” by making an *add-post* transaction, signing it with her app key and broadcasting it. Nodes verify that every transaction is correctly signed according to the specification. Common actions like deleting posts or following other users have their own transaction types. Snapchain transactions are self-authenticating and anyone trace the authenticity from the message to the app key to the wallet to the farcaster id.
Account recovery is built into registry contract which lets the wallet nominate another address which also controls the farcaster id. This could be set to the user's primary wallet, an m-of-n social recovery multisig or institutional recovery wallet. User may also compose their own recovery systems by converting the wallet into a smart wallet which can implement custom recovery logic.
#### 2. Transactions
A *blockchain transaction* is a Farcaster specific transactions that happens on an external blockchain. An example is when Alice makes a transaction to the registry contract to get her farcaster id and set up her app keys. Snapchain nodes listen to and store blockchain transactions in their history.
A *snapchain transaction* is a social action like making a new post. Alice says “Hello World” by making an *add-post* transaction, signing it with her app key and broadcasting it. Nodes verify that every transaction is correctly signed according to the specification. Common actions like deleting posts or following other users have their own transaction types. Snapchain transactions are self-authenticating and anyone trace the authenticity from the message to the app key to the wallet to the farcaster id.
 #### 3. Account State
An account comes into existence when a blockchain transaction is made to create a new account in the registry. It's state is simply the set of blockchain and snapchain transactions that it generates. A deterministic state root can be computed by putting all the transaction ids into a merkle trie. Transactions made by one account cannot affect the state of another account. Enforcing this restriction makes Snapchain more scalable since account-level sharding becomes trivial to implement.
When a new transaction is accepted, it may be added to the state or it may replace a previous transaction in the state or it may delete a previous transaction entirely.In the example below, we see Alice’s account state changing as she creates an account, adds a post and then deletes it.
#### 3. Account State
An account comes into existence when a blockchain transaction is made to create a new account in the registry. It's state is simply the set of blockchain and snapchain transactions that it generates. A deterministic state root can be computed by putting all the transaction ids into a merkle trie. Transactions made by one account cannot affect the state of another account. Enforcing this restriction makes Snapchain more scalable since account-level sharding becomes trivial to implement.
When a new transaction is accepted, it may be added to the state or it may replace a previous transaction in the state or it may delete a previous transaction entirely.In the example below, we see Alice’s account state changing as she creates an account, adds a post and then deletes it.
 *Formal definition: There exists a state (S) for an account (A) made up of transactions. S is a subset of all transactions made by a user (S ⊆ Ta). A merge function M accepts an S and t and returns a new state S’ (* M:S×t→S′)*. Each T is idempotent but not associative or commutative.*
#### 4. Blocks
Snapchain and blockchain transactions are sequenced into blocks. A block must have a signature from the block producer, a link to the previous block and a global state root. The global state root is the root of the global state trie, whose leaves are the roots of each account state trie. If the state of any account changes, the global state root also changes.
*Formal definition: There exists a state (S) for an account (A) made up of transactions. S is a subset of all transactions made by a user (S ⊆ Ta). A merge function M accepts an S and t and returns a new state S’ (* M:S×t→S′)*. Each T is idempotent but not associative or commutative.*
#### 4. Blocks
Snapchain and blockchain transactions are sequenced into blocks. A block must have a signature from the block producer, a link to the previous block and a global state root. The global state root is the root of the global state trie, whose leaves are the roots of each account state trie. If the state of any account changes, the global state root also changes.
 Blocks are produced by a committee of block validators and tendermint is used to reach consensus. A leader is chosen to produce the block and at least two-thirds of other validators must sign off. Snapchain is byzantine tolerant and up to one-third of the network can be malicious without affecting block production. Validators are selected through a voting committee which is described in Appendix A.
Blocks are grouped into epochs that are K blocks in length. A special epoch block is published at the beginning which contains additional metadata used to re-configure chain parameters. These blocks must be preserved forever and cannot be pruned. One example of epoch metadata is the leader rotation schedule. Leaders must be rotated periodically or if they fail to produce a block. The schedule for the next K blocks is determined using a deterministic function and included in every epoch block.
Nodes get new blocks from their peers and update account states. After a week, non-epoch blocks can be pruned by nodes to free up disk space. Pruning permanently removes deleted posts and likes which is desirable feature for users. The week’s delay ensures that nodes that go offline even for a few days can catch up by streaming blocks from their peers.
Nodes that go offline for long periods (or that start from scratch) must use snapshot sync instead. The protocol will publish daily snapshots of the global state to a file server as a public good. The snapshot is tamper-proof since modifying transactions will invalidate block signatures and omitting transactions will invalidate the global root. Nodes can download the state snapshot and then stream blocks from their peers to catch up.
#### 5. State Rent
Decentralized networks can be flooded with transactions which consume disk space, bandwidth and compute. Blockchains control this by imposing a per-transaction fee, but this isn’t great for a social network. If users have to worry about fees for each post, they will post less frequently which is bad for the network.
Snapchain gives users practically unlimited transactions if they pay a yearly fee. Users must rent a storage unit on the external blockchain after creating an account. Each unit gives them a rate limit (500 tx/hour) and a storage limit (10,000 txns) for their account state. Users can buy multiple units to increase these limits but in practice 99% of users rarely need more than one.
Usage feels “unlimited” because when storage limits are exceeded a user’s oldest transaction is discarded instead of preventing the newer transaction from confirming. Each transaction type (post, like, follow) has its own set of limits and a newer post will push out the oldest post. This generally works well in a timeline based social network because older posts are rarely revisited and most users are comfortable with the ephemeral behavior. Those who want more permanence can pay for additional storage units or archive data elsewhere.
The benefits of this system are that users don’t really have to think about storage and can just keep using the network. One downside is that a single storage unit must have separate, fixed limits for each types and users with different usage patterns may feel that they are wasting storage. Another downside is that while expiring the oldest message is a reasonable decision for posts, it may not be the right tradeoff for something like a follow. Apps may need to implement safeguards to protect users from blowing away certain historical data when limits are exceeded.
#### 6. Sharding
Snapchain can be sharded into N segments using N+1 tendermint chains to improve scalability. Accounts are assigned to a chain using a deterministic function. In the example below, odd numbered accounts are assigned to one shard and even ones to the other. The 0th chain is used to unite all the shards so that they appear as a single chain. Our approach to sharding is inspired by [NEAR’s Nightshade](https://pages.near.org/downloads/Nightshade.pdf).
Blocks are produced by a committee of block validators and tendermint is used to reach consensus. A leader is chosen to produce the block and at least two-thirds of other validators must sign off. Snapchain is byzantine tolerant and up to one-third of the network can be malicious without affecting block production. Validators are selected through a voting committee which is described in Appendix A.
Blocks are grouped into epochs that are K blocks in length. A special epoch block is published at the beginning which contains additional metadata used to re-configure chain parameters. These blocks must be preserved forever and cannot be pruned. One example of epoch metadata is the leader rotation schedule. Leaders must be rotated periodically or if they fail to produce a block. The schedule for the next K blocks is determined using a deterministic function and included in every epoch block.
Nodes get new blocks from their peers and update account states. After a week, non-epoch blocks can be pruned by nodes to free up disk space. Pruning permanently removes deleted posts and likes which is desirable feature for users. The week’s delay ensures that nodes that go offline even for a few days can catch up by streaming blocks from their peers.
Nodes that go offline for long periods (or that start from scratch) must use snapshot sync instead. The protocol will publish daily snapshots of the global state to a file server as a public good. The snapshot is tamper-proof since modifying transactions will invalidate block signatures and omitting transactions will invalidate the global root. Nodes can download the state snapshot and then stream blocks from their peers to catch up.
#### 5. State Rent
Decentralized networks can be flooded with transactions which consume disk space, bandwidth and compute. Blockchains control this by imposing a per-transaction fee, but this isn’t great for a social network. If users have to worry about fees for each post, they will post less frequently which is bad for the network.
Snapchain gives users practically unlimited transactions if they pay a yearly fee. Users must rent a storage unit on the external blockchain after creating an account. Each unit gives them a rate limit (500 tx/hour) and a storage limit (10,000 txns) for their account state. Users can buy multiple units to increase these limits but in practice 99% of users rarely need more than one.
Usage feels “unlimited” because when storage limits are exceeded a user’s oldest transaction is discarded instead of preventing the newer transaction from confirming. Each transaction type (post, like, follow) has its own set of limits and a newer post will push out the oldest post. This generally works well in a timeline based social network because older posts are rarely revisited and most users are comfortable with the ephemeral behavior. Those who want more permanence can pay for additional storage units or archive data elsewhere.
The benefits of this system are that users don’t really have to think about storage and can just keep using the network. One downside is that a single storage unit must have separate, fixed limits for each types and users with different usage patterns may feel that they are wasting storage. Another downside is that while expiring the oldest message is a reasonable decision for posts, it may not be the right tradeoff for something like a follow. Apps may need to implement safeguards to protect users from blowing away certain historical data when limits are exceeded.
#### 6. Sharding
Snapchain can be sharded into N segments using N+1 tendermint chains to improve scalability. Accounts are assigned to a chain using a deterministic function. In the example below, odd numbered accounts are assigned to one shard and even ones to the other. The 0th chain is used to unite all the shards so that they appear as a single chain. Our approach to sharding is inspired by [NEAR’s Nightshade](https://pages.near.org/downloads/Nightshade.pdf).
 A shard chain must have at least three validators and store all relevant account state. Validators may be automatically or manually rotated between shards through a validator schedule in the epoch block. Erasure coding is used to distribute account state from one shard across validators in other shards so that the data is still available even if all validators within a shard fail.
Block production is triggered when the previous block is finalized. Each shard chain bundles transactions into a block and computes a shard root, which is like the global root but limited to accounts in a shard. The 0th shard chain waits for the N shards to be produced and then performs another tendermint step bundling them into a single block and computes a global state root across the shard roots.
A shard chain must have at least three validators and store all relevant account state. Validators may be automatically or manually rotated between shards through a validator schedule in the epoch block. Erasure coding is used to distribute account state from one shard across validators in other shards so that the data is still available even if all validators within a shard fail.
Block production is triggered when the previous block is finalized. Each shard chain bundles transactions into a block and computes a shard root, which is like the global root but limited to accounts in a shard. The 0th shard chain waits for the N shards to be produced and then performs another tendermint step bundling them into a single block and computes a global state root across the shard roots.
 #### 7. Sync
Nodes rely on gossip as the primary mechanism for p2p communication. When a block is produced, the block is gossiped out separately from the shards that compose it. Gossip failures are reasonably easy to recover from due to ordering. If a block is skipped, a sequence jump will be detected and the node is aware that they missed a block. All nodes will expose rpc endpoints which can be used to fetch older blocks.
Validators also rely on gossip to manage the mempool and for inter-validator communication when consensus is being reached on the state of a block. All the tendermint consensus steps happen via gossip messages.
#### 8. Handling Failures
Validators can fail in a variety of ways and we must define how the network behaves in each scenario. Let’s start with the honest malfunctions:
* Shard leader fails to produce a shard — after 1 second, consensus changes leadership according to the rotation. We can tolerate the failure of up to 1/3 of the validators.
* A shard is not produced in time for the block — block production continues. If they fail to produce a shard for an entire epoch, the chain is halted.
* A block is not produced — after 1 seconds, consensus changes leadership according to the rotation. We can tolerate the failure of up to 1/3 of the block leaders.
If nodes are behaving maliciously, there are more attack scenarios that are possible:
* Block leader excludes shards or halts production — mitigated by rotating leaders, but governance action is needed to evict them permanently and solve the issue.
* Shard leader excludes a user’s transactions — mitigated by rotating shard leaders, but governance action is needed to evict them \* permanently and solve the issue.
* Shard validator majority excludes a user’s transactions — if more than 2/3rd of a validators shards collude they can censor a user, and governance action is needed to resolve.
* Block validator majority excludes a shard — if more than 2/3rd of block validators collude they can censor a shard, and governance action is needed to resolve.
* Shard validator majority can reissue a shard before block finality — TBD are malicious, they can reissue a shard for a block before it gets finalized.
* If > 2/3 majority of block validators and > 2/3 majority of one shard validators collude, they can reissue a block which would cause a network fork. Requires a refork and restart of the network,
#### 9. Upgrade process
New node versions are released frequently, and nodes are expected to be kept upto date. There are two kinds of version upgrades:
**Non-consensus breaking upgrades**
These are the most common kind, usually containing bug fixes or performance improvements. They are backwards compatible and there is no need to coordinate with other nodes. Nodes can be upgraded at any time and will continue to work with older nodes. These changes are denoted with a patch version bump (e.g. 0.1.0 -> 0.1.1).
**Consensus breaking upgrades**
These are less common and usually contain breaking changes to the protocol. The changes are not backwards compatible, and a node may halt if it's not upgraded. These changes are denoted with a minor version bump (e.g. 0.1.0 -> 0.2.0).
Each block contains a version number for the protocol in its header. When a consensus breaking change is required, a new minor version is released with a PROTOCOL\_VERSION bump and a timestamp after which it will take effect. All nodes must upgrade to the latest minor version before this time. All blocks produced on or after this timestamp will have this newer version. Nodes will not accept blocks with an unexpected version number and old nodes will detect they are out of date and self terminate.
**Accidental breaking changes**
It's also possible a bug or non-deterministic behaviour causes a breaking changes. E.g. a consensus breaking change is made without a corresponding protocol version bump. In this case, the nodes will proceed as normal until they encounter a blocks with the breaking change. At which point, the merkle roots will not match and the nodes that are not upgraded will halt. If this happens to validators, then block production will halt until a new version is released with a fix.
### Frequently Asked Questions
#### What exactly is hard about sync today?
A question that’s come up a few times about Snapchain is some variant of “why is syncing hard today?”
1. **There is no source of truth to sync from** - Messages can be added or removed from any node at any point in history due to the eventually consistent nature of CRDTs. Changes are gossiped out when they happen, but this could fail for a variety of reasons. The only way for a node to catch up 100% is to 1) sync with every other node and compare every message and 2) prevent messages from entering the network until this is completed. There are 4000 nodes x 150 million messages today with 100s of messages changing every second making this impossible.
2. **Rate limits cause nodes to diverge** — rate limits are important to protect the network since we do not charge transaction fees. global rate limiting is impossible with crdts, so they are implemented per node. It is possible for a message to be temporarily rejected from a hub due to rate limits, but accepted by others.
3. **Pruning complicates things** — pruning means that when one message is received another, older message might be removed. this means that older state is constantly being modified by newer messages so its hard to be efficient about comparing message ids and hard to reason about why two nodes diverge.
4. **Unidirectional sync is slow**. A node can be “ahead” of another node for some accounts state and “behind” it for another account. In order for these nodes to get into sync, both of them must pull data from the other node (bidirectional sync) before any state change happens. In practice, this is challenging to implementing and we rely on unidirectional sync which means that only some state converges.
One class of solutions was “partial ordering” — the basic idea was that we would chain messages by having each message reference the previous one. The chains would either be per user or per app, instead of the total ordering that Snapchain proposes. The benefit of this approach is that we do not need a heavyweight consensus model since in the happy path each chain is typically only edited by one node at a time.
One way to think about this is that it reduces the sync space. Our nodes today must compare the total set of messages which is 150M items. If you can have a chain per user, that’s down to 1M items. If you have a chain per app that’s probably closer to just \~1000 unique items to compare per sync.
But there are still some unsolved problems:
1. **Pruning is not possible** — because there is a chain, we cannot easily prune older state because the tombstones are necessary for sync to function.
2. **Rate limits are still hard** — there’s no way to reach consensus across users or apps, so the limits would still be local and diverge.
3. **Forking causes a lot of thrash** — a user or app can “fork” their chain by introducing a conflicting message at some point in history. This would invalidate all future messages, which causes a lot of sync thrash and is an easy way to DDOS the network.
4. **There is still no source of truth** — a node still has to sync with every other node to converge because we are using CRDTs. We have reduced the search space from 4000 nodes \* 150M items to 4000 nodes \* 1000 app chains. But nodes will still be slightly out of sync with each other, and the problem will return as we add more nodes or items.
5. **The migration path is messy** — since messages need to be chained to other messages, we have to update older messages to this new format. but the problem is that messages are signed, and unless the user comes online with their key the message cannot be upgraded. we cannot ensure that users return, so we must either deprecate older data after some cutoff or keep both sync models built into hubs for a really long time.
#### Why not fork a blockchain instead of designing a new one?
An alternative to building snapchain would be to fork an existing blockchain to have similar properties. We would modify the VM so that the set of opcodes is limited to social actions and modify the transaction model to mirror snapchains rate-limit + pruning approach to metering usage. There are two challenges with this approach:
1. **Sharding** - given our tx volume and data size, we're going to need sharding soon. snapchains can be sharded by account easily because transactions are independent across accounts. blockchains have much more complicated sharding systems and we haven't found any that work in production yet. so there's a lot of implementation risk and unnecessary complexity.
2. **Pruning** - most chains we've looked at don't really have an easy way to bolt on pruning, or the ability to arbitrarily discard data from points in time cleanly. we would have to do a large refactor that touches most abstractions in the system.
Blockchains are doing a lot of work in both these areas and it is quite possible that in 2-3 years our POV on this has changed. But if we are making a decision today about the best solution for a 5 year time horizon, Snapchain seems like a better bet.
#### Why was tendermint chosen as the consensus algorithm?
It has been used in production systems for many years, has fast finality and good liveness guarantees. There are also well written implementations in Go and even one in Rust.
#### Will validators be able to censor users?
Censorship will be challenging with as few as ten globally distributed validators. There is no direct economic gain or loss caused by censorship. Users being censored can amplify their message via others and censorship is provable by observing transactions in the mempool. If all validators do collude, the voting committee described in Section A acts as a check and balance to change the validators set. If all the validators and voters collude, it may be possible to censor.
#### Should we take a different approach that makes censorship even harder?
It is possible to design even more decentralized forms of governance and block production to make censorship less practical. The argument against this is that censorship is already reasonably impractical and most of these designs come with great cost to system complexity or user experience which makes the network less likely to be useful. It is also important to remember that Snapchain has been upgraded in the past as requirements have changed, and can be upgraded again in the future if necesary.
## Migrating to Snapchain from Hubble
Snapchain is designed to be a drop-in replacement for [Hubble](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/hub-monorepo). To migrate, follow these steps:
1. Set up a Snapchain node ([instructions](/guides/running-a-node)).
2. Update your app to use `hub-nodejs` with a version `>=0.13.0`
3. Update the connection url to talk the new snapchain host and port.
### Notable differences
1. Ports have changed. The HTTP port is `3381` and gRPC is `3383`.
2. `submitMessage` has a slightly different API and semantics, detailed below.
3. `HubEvent` ids no longer contain timestamps and calling `extractEventTimestamp` may return invalid data.
4. When calling `subscribe` or using shuttle, note that there are only 2 shards on snapchain and they are 1 indexed (shard 0 is chain metadata and does not have user data)
5. `hub-web` is not fully supported and may not work in some cases.
##### submitMessage
Messages once submitted must be included in blocks, similar to blockchain transactions. The `submitMessage` has two main differences from Hubble:
1. `submitMessage` requests must all contain `dataBytes` for Snapchain. The `hub-nodejs` builders handle this in all versions `>=0.13.0`, but if you're not using those you will need to manually update this like so:
```typescript
if (message.dataBytes === undefined) {
message.dataBytes = protobufs.MessageData.encode(message.data).finish();
message.data = undefined;
}
```
2. `submitMessage` is best-effort. It's possible, but rare, that `submitMessage` succeeds but the submitted message fails to get included in a block.
## Run Snapchain on AWS
:::tip
If your goal is to get started as quickly as possible, consider a managed service like [Neynar](https://neynar.com/) instead of running your own node.
:::
This guide will get you set up with a Snapchain node on an AWS EC2 instance and will cost roughly $100/month. You can run Snapchain on any server you like and costs may vary depending on provider.
### Launch a new instance
1. In AWS, go to EC2 > Instances > Launch Instances
2. Give it a name and select Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS (HVM), SSD Volume Type and 64-bit (x86). Choose m5.xlarge instance type .
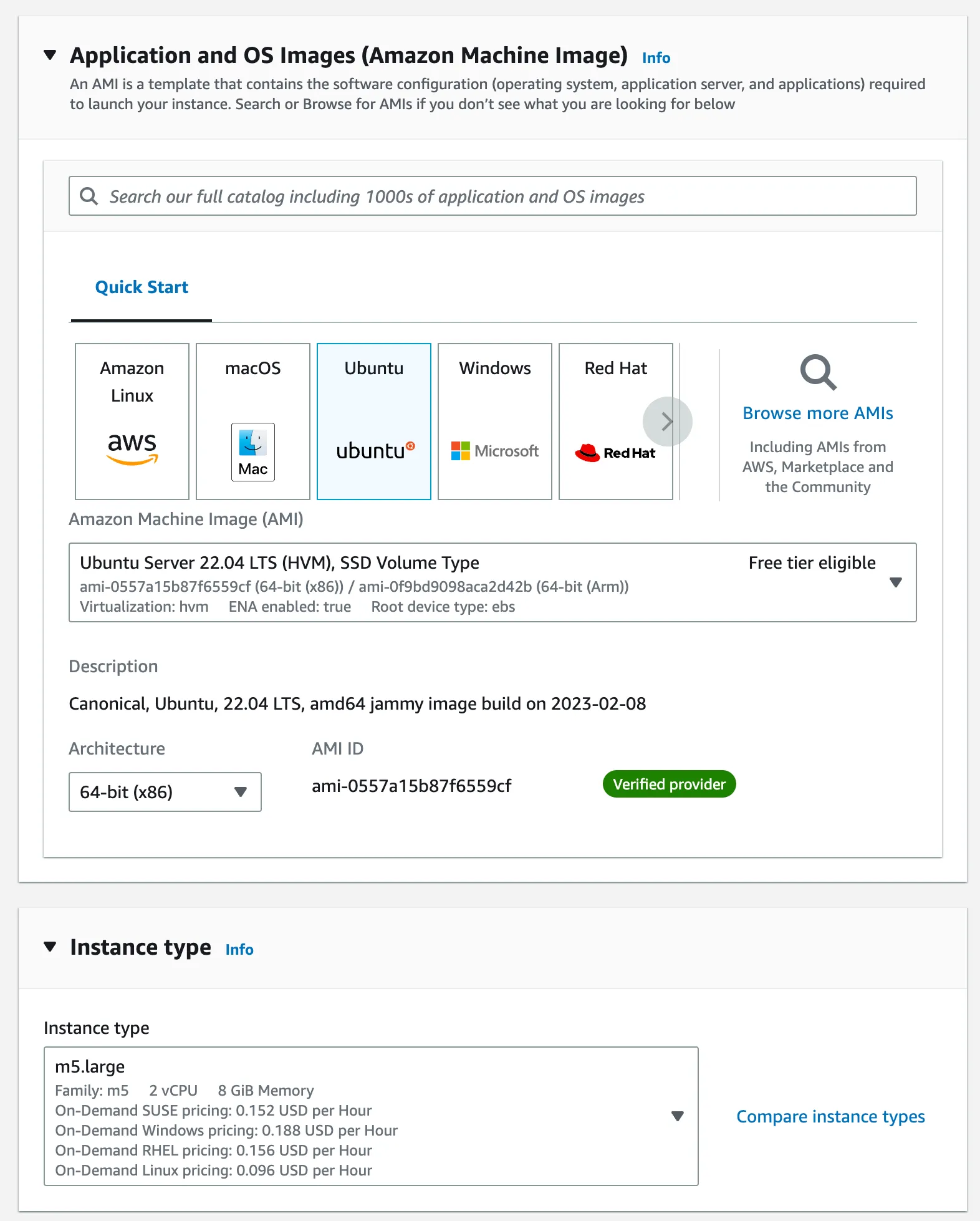
3. In Key pair (login), select Create a new key pair , then select RSA and .pem format, and save it
4. In Network settings, select Allow SSH traffic from Anywhere
5. In Configure storage, select 2 TB of gp3 storage.
6. Click Launch Instance on the right-hand side menu.
### Configure network firewall
1. Go to EC2 → Instances and find your instance
2. Click on the Instance ID
3. Click on Security > Security groups > (Security Group ID)
4. Click on Edit inbound rules and Edit outbound rules on the group page and add rules until they match the below.
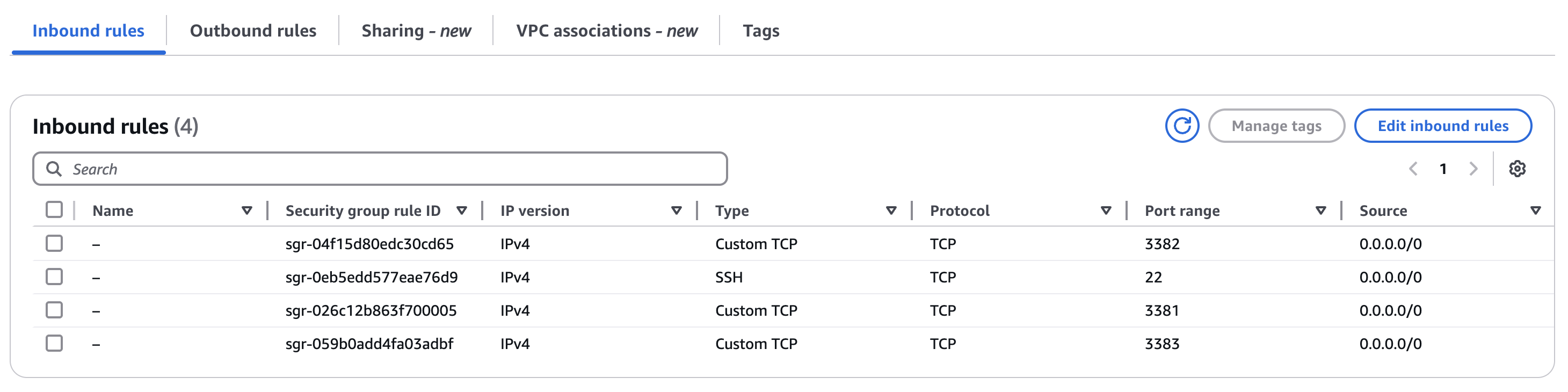
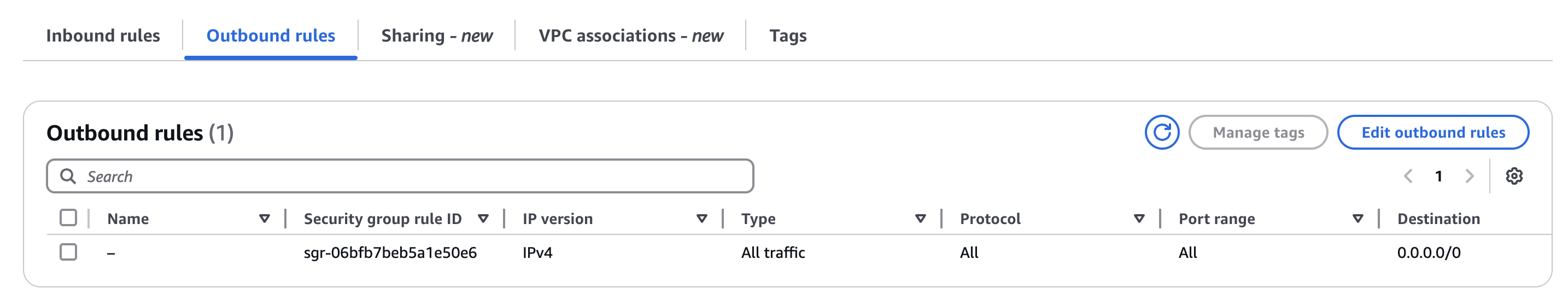
### Connect to your instance
1. Find your *.pem* file from earlier and run `chmod 400 key.pem`
2. Go to EC2 → Instances, click on the Instance ID and copy the IPv4 Address
3. Connect with `ssh ubuntu@ -i key.pem`
### Start syncing a node
```bash
# Install docker
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh
chmod +x get-docker.sh
./get-docker.sh
# Start Snapchain
mkdir snapchain && cd snapchain
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/farcasterxyz/snapchain/refs/heads/main/scripts/snapchain-bootstrap.sh | bash
```
Follow the remaining steps in [Getting Started](/getting-started) to validate and query your node.
## Sync Snapchain to Postgres
#### Pre-requisites
* Read access to a Snapchain node
See [running a node](/guides/running-a-node) for more information on how to set up a node.
While some applications can be written by directly querying Hubble, most serious applications need to access the data
in a more structured way.
[Shuttle](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/hub-monorepo/tree/main/packages/shuttle) is a package
that can be used to mirror Snapchain's data to a Postgres DB for convenient access to the underlying data.
### Quickstart
```bash
git clone git@github.com:farcasterxyz/hub-monorepo.git
# Ensure you have node 21 installed, use nvm to install it
nvm install 21
# If necessary, build packages/core dependency
( cd packages/core && yarn install && yarn build; )
# If necessary, build packages/hub-nodejs dependency
( cd packages/hub-nodejs && yarn install && yarn build; )
# Do remainder within the packages/shuttle directory
cd packages/shuttle
yarn install && yarn build
# Start the db dependencies
docker compose up postgres redis
# To perform reconciliation/backfill, start the worker (can run multiple processes to speed this up)
POSTGRES_URL=postgres://shuttle:password@0.0.0.0:6541 REDIS_URL=0.0.0.0:16379 HUB_HOST=: HUB_SSL=false yarn start worker
# Kick off the backfill process (configure with MAX_FID=100 or BACKFILL_FIDS=1,2,3)
POSTGRES_URL=postgres://shuttle:password@0.0.0.0:6541 REDIS_URL=0.0.0.0:16379 HUB_HOST=: HUB_SSL=false yarn start backfill
# Start the app and sync messages from the event stream
POSTGRES_URL=postgres://shuttle:password@0.0.0.0:6541 REDIS_URL=0.0.0.0:16379 HUB_HOST=: HUB_SSL=false yarn start start
```
This package is fully re-used from Hubble because the Snapchain APIs are backwards compatible with Hubble.
Check out the [documentation](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/hub-monorepo/blob/main/packages/shuttle/README.md) for more information.
## Writing to snapchain
Create your Farcaster account programmatically and publish your first message.
The example shows you how to:
* Make onchain transactions to create an account
* Rent a storage unit so you can publish messages
* Add signer key to sign messages
* Acquire an fname for your account
* Create, sign and publish messages
This example can be checked out as a fully functional
repository [here](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/hub-monorepo/tree/main/packages/hub-nodejs/examples/hello-world).
#### Requirements
* Write access to a node(either your own, or a 3rd party one)
* An ETH wallet with about \~10$ USD of ETH bridged to [Optimism](https://www.optimism.io/)
* An ETH RPC URL for OP Mainnet (e.g. via [Alchemy](https://www.alchemy.com/), [Infura](https://www.infura.io/) or [QuickNode](https://www.quicknode.com/)).
See [running a node](/guides/running-a-node) for more information on how to set up a node.
#### Custody address vs signer
In order to register an account and send messages, you need 2 pairs of keys:
* Custody: This is the ETH account which funds the initial id registration and storage. You need \~$10 USD in this account. You can use any ETH address as long as the $10 required is transferred via OP mainnet. The private key will be used to sign any signer requests and fname registrations. The person registering should always hold this private key.
* Signer: This is a keypair registered with the key registry that's used to sign messages a user publishes to the Farcaster network. If an app is publishing on behalf of a user, the app will hold the private key for this keypair.
### 1. Set up constants
```typescript
import {
ID_GATEWAY_ADDRESS,
idGatewayABI,
KEY_GATEWAY_ADDRESS,
keyGatewayABI,
ID_REGISTRY_ADDRESS,
idRegistryABI,
FarcasterNetwork,
} from '@farcaster/hub-web';
import { zeroAddress } from 'viem';
import { optimism } from 'viem/chains';
import { generatePrivateKey, privateKeyToAccount, toAccount } from "viem/accounts";
/**
* Populate the following constants with your own values
*/
const CUSTODY_PRIVATE_KEY = ''; // A private key corresponding with any ETH address.
const OP_PROVIDER_URL = ''; // Alchemy or Infura url
const RECOVERY_ADDRESS = zeroAddress; // Optional, using the default value means the account will not be recoverable later if the mnemonic is lost
const SIGNER_PRIVATE_KEY: Hex = zeroAddress; // Optional, using the default means a new signer will be created each time
// Note: crackle is the Farcaster team's mainnet node, which is password protected to prevent abuse. Use a 3rd party node
// provider like https://neynar.com/ Or, run your own mainnet node and broadcast to it permissionlessly.
const HUB_URL = 'crackle.farcaster.xyz:3383'; // URL + Port of the node
const HUB_USERNAME = ''; // Username for auth, leave blank if not using TLS
const HUB_PASS = ''; // Password for auth, leave blank if not using TLS
const USE_SSL = false; // set to true if talking to a node that uses SSL (3rd party hosted nodes or nodes that require auth)
const FC_NETWORK = FarcasterNetwork.MAINNET; // Network of the node
const CHAIN = optimism;
const IdGateway = {
abi: idGatewayABI,
address: ID_GATEWAY_ADDRESS,
chain: CHAIN,
};
const IdContract = {
abi: idRegistryABI,
address: ID_REGISTRY_ADDRESS,
chain: CHAIN,
};
const KeyContract = {
abi: keyGatewayABI,
address: KEY_GATEWAY_ADDRESS,
chain: CHAIN,
};
```
### 2. Register and pay for storage
Create a function to register an FID and pay for storage. This function will check if the account already has an FID
and return early if so.
If you don't have a funded account you can use, note the address and private key pair that's logged. Transfer funds to the address and use the same private key as the `CUSTODY_PRIVATE_KEY` for the next run of the script.
```typescript
const getOrRegisterFid = async (): Promise => {
const balance = await getBalance(walletClient, { address: account.address });
const existingFid = (await readContract(walletClient, {
...IdContract,
functionName: "idOf",
args: [account.address],
})) as bigint;
console.log(`Using address: ${account.address} with balance: ${balance}, private key: ${accountPrivateKey}`);
if (balance === 0n && existingFid === 0n) {
throw new Error("No existing Fid and no funds to register an fid");
}
if (existingFid > 0n) {
return parseInt(existingFid.toString());
}
const price = await readContract(walletClient, {
...IdGateway,
functionName: "price",
});
if (balance < price) {
throw new Error(`Insufficient balance to rent storage, required: ${price}, balance: ${balance}`);
}
const { request: registerRequest } = await simulateContract(walletClient, {
...IdGateway,
functionName: "register",
args: [RECOVERY_ADDRESS],
value: price,
});
const registerTxHash = await writeContract(walletClient, registerRequest);
const registerTxReceipt = await waitForTransactionReceipt(walletClient, { hash: registerTxHash });
if (registerTxReceipt.logs[0]) {
// Now extract the FID from the logs
const registerLog = decodeEventLog({
abi: idRegistryABI,
data: registerTxReceipt.logs[0].data,
topics: registerTxReceipt.logs[0].topics,
});
const fid = parseInt(registerLog.args["id"]);
return fid;
} else {
throw new Error("Did not receive logs for registered fid");
}
};
const fid = await getOrRegisterFid();
```
### 3. Add a signer
Now, we will add a signer to the key registry. Every signer must have a signed metadata field from the fid of the app requesting it.
In our case, we will use our own fid. Note, this requires you to sign a message with the private key of the address
holding the fid. If this is not possible, register a separate fid for the app first and use that.
```typescript
const getOrRegisterSigner = async (fid: number) => {
if (SIGNER_PRIVATE_KEY !== zeroAddress) {
// If a private key is provided, we assume the signer is already in the key registry
const privateKeyBytes = fromHex(SIGNER_PRIVATE_KEY, "bytes");
const publicKeyBytes = ed25519.getPublicKey(privateKeyBytes);
return privateKeyBytes;
}
const privateKey = ed25519.utils.randomPrivateKey();
const publicKey = toHex(ed25519.getPublicKey(privateKey));
// To add a key, we need to sign the metadata with the fid of the app we're adding the key on behalf of
// We'll use our own fid and custody address for simplicity. This can also be a separate App specific fid.
const localAccount = toAccount(account);
const eip712signer = new ViemLocalEip712Signer(localAccount);
const metadata = await eip712signer.getSignedKeyRequestMetadata({
requestFid: BigInt(fid),
key: fromHex(publicKey, "bytes"),
deadline: BigInt(Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000) + 60 * 60), // 1 hour from now
});
const metadataHex = toHex(metadata.unwrapOr(new Uint8Array()));
const { request: signerAddRequest } = await simulateContract(walletClient, {
...KeyContract,
functionName: "add",
args: [1, publicKey, 1, metadataHex], // keyType, publicKey, metadataType, metadata
});
const signerAddTxHash = await writeContract(walletClient, signerAddRequest);
await waitForTransactionReceipt(walletClient, { hash: signerAddTxHash });
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 30000));
return privateKey;
};
const signer = await getOrRegisterSigner(fid);
```
### 4. Register an fname
Now that the onchain actions are complete, let's register an fname using the farcaster offchain fname registry.
Registering an fname requires a signature from the custody address of the fid.
```typescript
const registerFname = async (fid: number) => {
try {
// First check if this fid already has an fname
const response = await axios.get(`https://fnames.farcaster.xyz/transfers/current?fid=${fid}`);
const fname = response.data.transfer.username;
return fname;
} catch (e) {
// No username, ignore and continue with registering
}
const fname = `fid-${fid}`;
const timestamp = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000);
const localAccount = toAccount(account);
const signer = new ViemLocalEip712Signer(localAccount as LocalAccount);
const userNameProofSignature = await signer.signUserNameProofClaim(
makeUserNameProofClaim({
name: fname,
timestamp: timestamp,
owner: account.address,
}),
);
try {
const response = await axios.post("https://fnames.farcaster.xyz/transfers", {
name: fname, // Name to register
from: 0, // Fid to transfer from (0 for a new registration)
to: fid, // Fid to transfer to (0 to unregister)
fid: fid, // Fid making the request (must match from or to)
owner: account.address, // Custody address of fid making the request
timestamp: timestamp, // Current timestamp in seconds
signature: bytesToHex(userNameProofSignature._unsafeUnwrap()), // EIP-712 signature signed by the current custody address of the fid
});
return fname;
} catch (e) {
// @ts-ignore
throw new Error(`Error registering fname: ${JSON.stringify(e.response.data)} (status: ${e.response.status})`);
}
};
const fname = await registerFname(fid);
```
Note that this only associated the name to our fid, we still need to set it as our username.
### 5. Write to Snapchain
Finally, we're now ready to submit messages. First, we shall set the fname as our username. And then post a
cast.
```typescript
const submitMessage = async (resultPromise: HubAsyncResult) => {
const result = await resultPromise;
if (result.isErr()) {
throw new Error(`Error creating message: ${result.error}`);
}
const messageSubmitResult = await hubClient.submitMessage(result.value, metadata);
if (messageSubmitResult.isErr()) {
throw new Error(`Error submitting message to node: ${messageSubmitResult.error}`);
}
};
const signer = new NobleEd25519Signer(signerPrivateKey);
const dataOptions = {
fid: fid,
network: FC_NETWORK,
};
const userDataPfpBody = {
type: UserDataType.USERNAME,
value: fname,
};
await submitMessage(makeUserDataAdd(userDataPfpBody, dataOptions, signer));
await submitMessage(
makeCastAdd(
{
text: "Hello World!",
embeds: [],
embedsDeprecated: [],
mentions: [],
mentionsPositions: [],
type: CastType.CAST,
},
dataOptions,
signer,
));
```
Now, you can view your profile on any farcaster client. To see it on Warpcast, visit `https://warpcast.com/@`
## Events
Events represent state changes, like a new message or contract event.
Snapchain nodes emit events whenever they observe a state change. Clients can subscribe to a node using the [Events API](../grpcapi/events.md) to get a live stream of changes.
Snapchain keeps events around for 3 days after which they are deleted to save space. To get older data, use the [GRPC](../grpcapi/grpcapi.md) or [HTTP](../httpapi/httpapi.md) APIs.
### HubEvent
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----- | ------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| type | [HubEventType](#HubEventType) | | The type of event |
| id | [uint64](#uint64) | | Unique identifier for the event that encodes block height ordering |
| block\_number | [uint64](#uint64) | | The block number when the event was created |
| shard\_index | [uint32](#uint32) | | The shard index where the event occurred |
| timestamp | [uint64](#uint64) | | The timestamp when the event was created |
| body | [MergeMessageBody](#mergemessagebody),
#### 7. Sync
Nodes rely on gossip as the primary mechanism for p2p communication. When a block is produced, the block is gossiped out separately from the shards that compose it. Gossip failures are reasonably easy to recover from due to ordering. If a block is skipped, a sequence jump will be detected and the node is aware that they missed a block. All nodes will expose rpc endpoints which can be used to fetch older blocks.
Validators also rely on gossip to manage the mempool and for inter-validator communication when consensus is being reached on the state of a block. All the tendermint consensus steps happen via gossip messages.
#### 8. Handling Failures
Validators can fail in a variety of ways and we must define how the network behaves in each scenario. Let’s start with the honest malfunctions:
* Shard leader fails to produce a shard — after 1 second, consensus changes leadership according to the rotation. We can tolerate the failure of up to 1/3 of the validators.
* A shard is not produced in time for the block — block production continues. If they fail to produce a shard for an entire epoch, the chain is halted.
* A block is not produced — after 1 seconds, consensus changes leadership according to the rotation. We can tolerate the failure of up to 1/3 of the block leaders.
If nodes are behaving maliciously, there are more attack scenarios that are possible:
* Block leader excludes shards or halts production — mitigated by rotating leaders, but governance action is needed to evict them permanently and solve the issue.
* Shard leader excludes a user’s transactions — mitigated by rotating shard leaders, but governance action is needed to evict them \* permanently and solve the issue.
* Shard validator majority excludes a user’s transactions — if more than 2/3rd of a validators shards collude they can censor a user, and governance action is needed to resolve.
* Block validator majority excludes a shard — if more than 2/3rd of block validators collude they can censor a shard, and governance action is needed to resolve.
* Shard validator majority can reissue a shard before block finality — TBD are malicious, they can reissue a shard for a block before it gets finalized.
* If > 2/3 majority of block validators and > 2/3 majority of one shard validators collude, they can reissue a block which would cause a network fork. Requires a refork and restart of the network,
#### 9. Upgrade process
New node versions are released frequently, and nodes are expected to be kept upto date. There are two kinds of version upgrades:
**Non-consensus breaking upgrades**
These are the most common kind, usually containing bug fixes or performance improvements. They are backwards compatible and there is no need to coordinate with other nodes. Nodes can be upgraded at any time and will continue to work with older nodes. These changes are denoted with a patch version bump (e.g. 0.1.0 -> 0.1.1).
**Consensus breaking upgrades**
These are less common and usually contain breaking changes to the protocol. The changes are not backwards compatible, and a node may halt if it's not upgraded. These changes are denoted with a minor version bump (e.g. 0.1.0 -> 0.2.0).
Each block contains a version number for the protocol in its header. When a consensus breaking change is required, a new minor version is released with a PROTOCOL\_VERSION bump and a timestamp after which it will take effect. All nodes must upgrade to the latest minor version before this time. All blocks produced on or after this timestamp will have this newer version. Nodes will not accept blocks with an unexpected version number and old nodes will detect they are out of date and self terminate.
**Accidental breaking changes**
It's also possible a bug or non-deterministic behaviour causes a breaking changes. E.g. a consensus breaking change is made without a corresponding protocol version bump. In this case, the nodes will proceed as normal until they encounter a blocks with the breaking change. At which point, the merkle roots will not match and the nodes that are not upgraded will halt. If this happens to validators, then block production will halt until a new version is released with a fix.
### Frequently Asked Questions
#### What exactly is hard about sync today?
A question that’s come up a few times about Snapchain is some variant of “why is syncing hard today?”
1. **There is no source of truth to sync from** - Messages can be added or removed from any node at any point in history due to the eventually consistent nature of CRDTs. Changes are gossiped out when they happen, but this could fail for a variety of reasons. The only way for a node to catch up 100% is to 1) sync with every other node and compare every message and 2) prevent messages from entering the network until this is completed. There are 4000 nodes x 150 million messages today with 100s of messages changing every second making this impossible.
2. **Rate limits cause nodes to diverge** — rate limits are important to protect the network since we do not charge transaction fees. global rate limiting is impossible with crdts, so they are implemented per node. It is possible for a message to be temporarily rejected from a hub due to rate limits, but accepted by others.
3. **Pruning complicates things** — pruning means that when one message is received another, older message might be removed. this means that older state is constantly being modified by newer messages so its hard to be efficient about comparing message ids and hard to reason about why two nodes diverge.
4. **Unidirectional sync is slow**. A node can be “ahead” of another node for some accounts state and “behind” it for another account. In order for these nodes to get into sync, both of them must pull data from the other node (bidirectional sync) before any state change happens. In practice, this is challenging to implementing and we rely on unidirectional sync which means that only some state converges.
One class of solutions was “partial ordering” — the basic idea was that we would chain messages by having each message reference the previous one. The chains would either be per user or per app, instead of the total ordering that Snapchain proposes. The benefit of this approach is that we do not need a heavyweight consensus model since in the happy path each chain is typically only edited by one node at a time.
One way to think about this is that it reduces the sync space. Our nodes today must compare the total set of messages which is 150M items. If you can have a chain per user, that’s down to 1M items. If you have a chain per app that’s probably closer to just \~1000 unique items to compare per sync.
But there are still some unsolved problems:
1. **Pruning is not possible** — because there is a chain, we cannot easily prune older state because the tombstones are necessary for sync to function.
2. **Rate limits are still hard** — there’s no way to reach consensus across users or apps, so the limits would still be local and diverge.
3. **Forking causes a lot of thrash** — a user or app can “fork” their chain by introducing a conflicting message at some point in history. This would invalidate all future messages, which causes a lot of sync thrash and is an easy way to DDOS the network.
4. **There is still no source of truth** — a node still has to sync with every other node to converge because we are using CRDTs. We have reduced the search space from 4000 nodes \* 150M items to 4000 nodes \* 1000 app chains. But nodes will still be slightly out of sync with each other, and the problem will return as we add more nodes or items.
5. **The migration path is messy** — since messages need to be chained to other messages, we have to update older messages to this new format. but the problem is that messages are signed, and unless the user comes online with their key the message cannot be upgraded. we cannot ensure that users return, so we must either deprecate older data after some cutoff or keep both sync models built into hubs for a really long time.
#### Why not fork a blockchain instead of designing a new one?
An alternative to building snapchain would be to fork an existing blockchain to have similar properties. We would modify the VM so that the set of opcodes is limited to social actions and modify the transaction model to mirror snapchains rate-limit + pruning approach to metering usage. There are two challenges with this approach:
1. **Sharding** - given our tx volume and data size, we're going to need sharding soon. snapchains can be sharded by account easily because transactions are independent across accounts. blockchains have much more complicated sharding systems and we haven't found any that work in production yet. so there's a lot of implementation risk and unnecessary complexity.
2. **Pruning** - most chains we've looked at don't really have an easy way to bolt on pruning, or the ability to arbitrarily discard data from points in time cleanly. we would have to do a large refactor that touches most abstractions in the system.
Blockchains are doing a lot of work in both these areas and it is quite possible that in 2-3 years our POV on this has changed. But if we are making a decision today about the best solution for a 5 year time horizon, Snapchain seems like a better bet.
#### Why was tendermint chosen as the consensus algorithm?
It has been used in production systems for many years, has fast finality and good liveness guarantees. There are also well written implementations in Go and even one in Rust.
#### Will validators be able to censor users?
Censorship will be challenging with as few as ten globally distributed validators. There is no direct economic gain or loss caused by censorship. Users being censored can amplify their message via others and censorship is provable by observing transactions in the mempool. If all validators do collude, the voting committee described in Section A acts as a check and balance to change the validators set. If all the validators and voters collude, it may be possible to censor.
#### Should we take a different approach that makes censorship even harder?
It is possible to design even more decentralized forms of governance and block production to make censorship less practical. The argument against this is that censorship is already reasonably impractical and most of these designs come with great cost to system complexity or user experience which makes the network less likely to be useful. It is also important to remember that Snapchain has been upgraded in the past as requirements have changed, and can be upgraded again in the future if necesary.
## Migrating to Snapchain from Hubble
Snapchain is designed to be a drop-in replacement for [Hubble](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/hub-monorepo). To migrate, follow these steps:
1. Set up a Snapchain node ([instructions](/guides/running-a-node)).
2. Update your app to use `hub-nodejs` with a version `>=0.13.0`
3. Update the connection url to talk the new snapchain host and port.
### Notable differences
1. Ports have changed. The HTTP port is `3381` and gRPC is `3383`.
2. `submitMessage` has a slightly different API and semantics, detailed below.
3. `HubEvent` ids no longer contain timestamps and calling `extractEventTimestamp` may return invalid data.
4. When calling `subscribe` or using shuttle, note that there are only 2 shards on snapchain and they are 1 indexed (shard 0 is chain metadata and does not have user data)
5. `hub-web` is not fully supported and may not work in some cases.
##### submitMessage
Messages once submitted must be included in blocks, similar to blockchain transactions. The `submitMessage` has two main differences from Hubble:
1. `submitMessage` requests must all contain `dataBytes` for Snapchain. The `hub-nodejs` builders handle this in all versions `>=0.13.0`, but if you're not using those you will need to manually update this like so:
```typescript
if (message.dataBytes === undefined) {
message.dataBytes = protobufs.MessageData.encode(message.data).finish();
message.data = undefined;
}
```
2. `submitMessage` is best-effort. It's possible, but rare, that `submitMessage` succeeds but the submitted message fails to get included in a block.
## Run Snapchain on AWS
:::tip
If your goal is to get started as quickly as possible, consider a managed service like [Neynar](https://neynar.com/) instead of running your own node.
:::
This guide will get you set up with a Snapchain node on an AWS EC2 instance and will cost roughly $100/month. You can run Snapchain on any server you like and costs may vary depending on provider.
### Launch a new instance
1. In AWS, go to EC2 > Instances > Launch Instances
2. Give it a name and select Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS (HVM), SSD Volume Type and 64-bit (x86). Choose m5.xlarge instance type .

3. In Key pair (login), select Create a new key pair , then select RSA and .pem format, and save it
4. In Network settings, select Allow SSH traffic from Anywhere
5. In Configure storage, select 2 TB of gp3 storage.
6. Click Launch Instance on the right-hand side menu.
### Configure network firewall
1. Go to EC2 → Instances and find your instance
2. Click on the Instance ID
3. Click on Security > Security groups > (Security Group ID)
4. Click on Edit inbound rules and Edit outbound rules on the group page and add rules until they match the below.


### Connect to your instance
1. Find your *.pem* file from earlier and run `chmod 400 key.pem`
2. Go to EC2 → Instances, click on the Instance ID and copy the IPv4 Address
3. Connect with `ssh ubuntu@ -i key.pem`
### Start syncing a node
```bash
# Install docker
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh
chmod +x get-docker.sh
./get-docker.sh
# Start Snapchain
mkdir snapchain && cd snapchain
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/farcasterxyz/snapchain/refs/heads/main/scripts/snapchain-bootstrap.sh | bash
```
Follow the remaining steps in [Getting Started](/getting-started) to validate and query your node.
## Sync Snapchain to Postgres
#### Pre-requisites
* Read access to a Snapchain node
See [running a node](/guides/running-a-node) for more information on how to set up a node.
While some applications can be written by directly querying Hubble, most serious applications need to access the data
in a more structured way.
[Shuttle](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/hub-monorepo/tree/main/packages/shuttle) is a package
that can be used to mirror Snapchain's data to a Postgres DB for convenient access to the underlying data.
### Quickstart
```bash
git clone git@github.com:farcasterxyz/hub-monorepo.git
# Ensure you have node 21 installed, use nvm to install it
nvm install 21
# If necessary, build packages/core dependency
( cd packages/core && yarn install && yarn build; )
# If necessary, build packages/hub-nodejs dependency
( cd packages/hub-nodejs && yarn install && yarn build; )
# Do remainder within the packages/shuttle directory
cd packages/shuttle
yarn install && yarn build
# Start the db dependencies
docker compose up postgres redis
# To perform reconciliation/backfill, start the worker (can run multiple processes to speed this up)
POSTGRES_URL=postgres://shuttle:password@0.0.0.0:6541 REDIS_URL=0.0.0.0:16379 HUB_HOST=: HUB_SSL=false yarn start worker
# Kick off the backfill process (configure with MAX_FID=100 or BACKFILL_FIDS=1,2,3)
POSTGRES_URL=postgres://shuttle:password@0.0.0.0:6541 REDIS_URL=0.0.0.0:16379 HUB_HOST=: HUB_SSL=false yarn start backfill
# Start the app and sync messages from the event stream
POSTGRES_URL=postgres://shuttle:password@0.0.0.0:6541 REDIS_URL=0.0.0.0:16379 HUB_HOST=: HUB_SSL=false yarn start start
```
This package is fully re-used from Hubble because the Snapchain APIs are backwards compatible with Hubble.
Check out the [documentation](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/hub-monorepo/blob/main/packages/shuttle/README.md) for more information.
## Writing to snapchain
Create your Farcaster account programmatically and publish your first message.
The example shows you how to:
* Make onchain transactions to create an account
* Rent a storage unit so you can publish messages
* Add signer key to sign messages
* Acquire an fname for your account
* Create, sign and publish messages
This example can be checked out as a fully functional
repository [here](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/hub-monorepo/tree/main/packages/hub-nodejs/examples/hello-world).
#### Requirements
* Write access to a node(either your own, or a 3rd party one)
* An ETH wallet with about \~10$ USD of ETH bridged to [Optimism](https://www.optimism.io/)
* An ETH RPC URL for OP Mainnet (e.g. via [Alchemy](https://www.alchemy.com/), [Infura](https://www.infura.io/) or [QuickNode](https://www.quicknode.com/)).
See [running a node](/guides/running-a-node) for more information on how to set up a node.
#### Custody address vs signer
In order to register an account and send messages, you need 2 pairs of keys:
* Custody: This is the ETH account which funds the initial id registration and storage. You need \~$10 USD in this account. You can use any ETH address as long as the $10 required is transferred via OP mainnet. The private key will be used to sign any signer requests and fname registrations. The person registering should always hold this private key.
* Signer: This is a keypair registered with the key registry that's used to sign messages a user publishes to the Farcaster network. If an app is publishing on behalf of a user, the app will hold the private key for this keypair.
### 1. Set up constants
```typescript
import {
ID_GATEWAY_ADDRESS,
idGatewayABI,
KEY_GATEWAY_ADDRESS,
keyGatewayABI,
ID_REGISTRY_ADDRESS,
idRegistryABI,
FarcasterNetwork,
} from '@farcaster/hub-web';
import { zeroAddress } from 'viem';
import { optimism } from 'viem/chains';
import { generatePrivateKey, privateKeyToAccount, toAccount } from "viem/accounts";
/**
* Populate the following constants with your own values
*/
const CUSTODY_PRIVATE_KEY = ''; // A private key corresponding with any ETH address.
const OP_PROVIDER_URL = ''; // Alchemy or Infura url
const RECOVERY_ADDRESS = zeroAddress; // Optional, using the default value means the account will not be recoverable later if the mnemonic is lost
const SIGNER_PRIVATE_KEY: Hex = zeroAddress; // Optional, using the default means a new signer will be created each time
// Note: crackle is the Farcaster team's mainnet node, which is password protected to prevent abuse. Use a 3rd party node
// provider like https://neynar.com/ Or, run your own mainnet node and broadcast to it permissionlessly.
const HUB_URL = 'crackle.farcaster.xyz:3383'; // URL + Port of the node
const HUB_USERNAME = ''; // Username for auth, leave blank if not using TLS
const HUB_PASS = ''; // Password for auth, leave blank if not using TLS
const USE_SSL = false; // set to true if talking to a node that uses SSL (3rd party hosted nodes or nodes that require auth)
const FC_NETWORK = FarcasterNetwork.MAINNET; // Network of the node
const CHAIN = optimism;
const IdGateway = {
abi: idGatewayABI,
address: ID_GATEWAY_ADDRESS,
chain: CHAIN,
};
const IdContract = {
abi: idRegistryABI,
address: ID_REGISTRY_ADDRESS,
chain: CHAIN,
};
const KeyContract = {
abi: keyGatewayABI,
address: KEY_GATEWAY_ADDRESS,
chain: CHAIN,
};
```
### 2. Register and pay for storage
Create a function to register an FID and pay for storage. This function will check if the account already has an FID
and return early if so.
If you don't have a funded account you can use, note the address and private key pair that's logged. Transfer funds to the address and use the same private key as the `CUSTODY_PRIVATE_KEY` for the next run of the script.
```typescript
const getOrRegisterFid = async (): Promise => {
const balance = await getBalance(walletClient, { address: account.address });
const existingFid = (await readContract(walletClient, {
...IdContract,
functionName: "idOf",
args: [account.address],
})) as bigint;
console.log(`Using address: ${account.address} with balance: ${balance}, private key: ${accountPrivateKey}`);
if (balance === 0n && existingFid === 0n) {
throw new Error("No existing Fid and no funds to register an fid");
}
if (existingFid > 0n) {
return parseInt(existingFid.toString());
}
const price = await readContract(walletClient, {
...IdGateway,
functionName: "price",
});
if (balance < price) {
throw new Error(`Insufficient balance to rent storage, required: ${price}, balance: ${balance}`);
}
const { request: registerRequest } = await simulateContract(walletClient, {
...IdGateway,
functionName: "register",
args: [RECOVERY_ADDRESS],
value: price,
});
const registerTxHash = await writeContract(walletClient, registerRequest);
const registerTxReceipt = await waitForTransactionReceipt(walletClient, { hash: registerTxHash });
if (registerTxReceipt.logs[0]) {
// Now extract the FID from the logs
const registerLog = decodeEventLog({
abi: idRegistryABI,
data: registerTxReceipt.logs[0].data,
topics: registerTxReceipt.logs[0].topics,
});
const fid = parseInt(registerLog.args["id"]);
return fid;
} else {
throw new Error("Did not receive logs for registered fid");
}
};
const fid = await getOrRegisterFid();
```
### 3. Add a signer
Now, we will add a signer to the key registry. Every signer must have a signed metadata field from the fid of the app requesting it.
In our case, we will use our own fid. Note, this requires you to sign a message with the private key of the address
holding the fid. If this is not possible, register a separate fid for the app first and use that.
```typescript
const getOrRegisterSigner = async (fid: number) => {
if (SIGNER_PRIVATE_KEY !== zeroAddress) {
// If a private key is provided, we assume the signer is already in the key registry
const privateKeyBytes = fromHex(SIGNER_PRIVATE_KEY, "bytes");
const publicKeyBytes = ed25519.getPublicKey(privateKeyBytes);
return privateKeyBytes;
}
const privateKey = ed25519.utils.randomPrivateKey();
const publicKey = toHex(ed25519.getPublicKey(privateKey));
// To add a key, we need to sign the metadata with the fid of the app we're adding the key on behalf of
// We'll use our own fid and custody address for simplicity. This can also be a separate App specific fid.
const localAccount = toAccount(account);
const eip712signer = new ViemLocalEip712Signer(localAccount);
const metadata = await eip712signer.getSignedKeyRequestMetadata({
requestFid: BigInt(fid),
key: fromHex(publicKey, "bytes"),
deadline: BigInt(Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000) + 60 * 60), // 1 hour from now
});
const metadataHex = toHex(metadata.unwrapOr(new Uint8Array()));
const { request: signerAddRequest } = await simulateContract(walletClient, {
...KeyContract,
functionName: "add",
args: [1, publicKey, 1, metadataHex], // keyType, publicKey, metadataType, metadata
});
const signerAddTxHash = await writeContract(walletClient, signerAddRequest);
await waitForTransactionReceipt(walletClient, { hash: signerAddTxHash });
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 30000));
return privateKey;
};
const signer = await getOrRegisterSigner(fid);
```
### 4. Register an fname
Now that the onchain actions are complete, let's register an fname using the farcaster offchain fname registry.
Registering an fname requires a signature from the custody address of the fid.
```typescript
const registerFname = async (fid: number) => {
try {
// First check if this fid already has an fname
const response = await axios.get(`https://fnames.farcaster.xyz/transfers/current?fid=${fid}`);
const fname = response.data.transfer.username;
return fname;
} catch (e) {
// No username, ignore and continue with registering
}
const fname = `fid-${fid}`;
const timestamp = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000);
const localAccount = toAccount(account);
const signer = new ViemLocalEip712Signer(localAccount as LocalAccount);
const userNameProofSignature = await signer.signUserNameProofClaim(
makeUserNameProofClaim({
name: fname,
timestamp: timestamp,
owner: account.address,
}),
);
try {
const response = await axios.post("https://fnames.farcaster.xyz/transfers", {
name: fname, // Name to register
from: 0, // Fid to transfer from (0 for a new registration)
to: fid, // Fid to transfer to (0 to unregister)
fid: fid, // Fid making the request (must match from or to)
owner: account.address, // Custody address of fid making the request
timestamp: timestamp, // Current timestamp in seconds
signature: bytesToHex(userNameProofSignature._unsafeUnwrap()), // EIP-712 signature signed by the current custody address of the fid
});
return fname;
} catch (e) {
// @ts-ignore
throw new Error(`Error registering fname: ${JSON.stringify(e.response.data)} (status: ${e.response.status})`);
}
};
const fname = await registerFname(fid);
```
Note that this only associated the name to our fid, we still need to set it as our username.
### 5. Write to Snapchain
Finally, we're now ready to submit messages. First, we shall set the fname as our username. And then post a
cast.
```typescript
const submitMessage = async (resultPromise: HubAsyncResult) => {
const result = await resultPromise;
if (result.isErr()) {
throw new Error(`Error creating message: ${result.error}`);
}
const messageSubmitResult = await hubClient.submitMessage(result.value, metadata);
if (messageSubmitResult.isErr()) {
throw new Error(`Error submitting message to node: ${messageSubmitResult.error}`);
}
};
const signer = new NobleEd25519Signer(signerPrivateKey);
const dataOptions = {
fid: fid,
network: FC_NETWORK,
};
const userDataPfpBody = {
type: UserDataType.USERNAME,
value: fname,
};
await submitMessage(makeUserDataAdd(userDataPfpBody, dataOptions, signer));
await submitMessage(
makeCastAdd(
{
text: "Hello World!",
embeds: [],
embedsDeprecated: [],
mentions: [],
mentionsPositions: [],
type: CastType.CAST,
},
dataOptions,
signer,
));
```
Now, you can view your profile on any farcaster client. To see it on Warpcast, visit `https://warpcast.com/@`
## Events
Events represent state changes, like a new message or contract event.
Snapchain nodes emit events whenever they observe a state change. Clients can subscribe to a node using the [Events API](../grpcapi/events.md) to get a live stream of changes.
Snapchain keeps events around for 3 days after which they are deleted to save space. To get older data, use the [GRPC](../grpcapi/grpcapi.md) or [HTTP](../httpapi/httpapi.md) APIs.
### HubEvent
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----- | ------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| type | [HubEventType](#HubEventType) | | The type of event |
| id | [uint64](#uint64) | | Unique identifier for the event that encodes block height ordering |
| block\_number | [uint64](#uint64) | | The block number when the event was created |
| shard\_index | [uint32](#uint32) | | The shard index where the event occurred |
| timestamp | [uint64](#uint64) | | The timestamp when the event was created |
| body | [MergeMessageBody](#mergemessagebody),
[PruneMessageBody](#prunemessagebody),
[RevokeMessageBody](#revokemessagebody),
[MergeUserNameProofBody](#mergeusernameproofbody),
[MergeOnChainEventBody](#mergeonchaineventbody),
[MergeFailureBody](#mergefailurebody),
[BlockConfirmedBody](#blockconfirmedbody) | oneOf | The event payload |
#### Event ID Construction
Event IDs are constructed to ensure chronological ordering by block. The ID combines:
* The block height (when the event was created)
* A sequence number within that block
This design allows clients to determine which events occurred in the same block and their relative order, which is useful for processing events in chronological sequence.
### HubEventType
| Name | Number | Description |
| ----------------------------------------- | ------ | ----------- |
| HUB\_EVENT\_TYPE\_NONE | 0 | |
| HUB\_EVENT\_TYPE\_MERGE\_MESSAGE | 1 | |
| HUB\_EVENT\_TYPE\_PRUNE\_MESSAGE | 2 | |
| HUB\_EVENT\_TYPE\_REVOKE\_MESSAGE | 3 | |
| HUB\_EVENT\_TYPE\_MERGE\_USERNAME\_PROOF | 6 | |
| HUB\_EVENT\_TYPE\_MERGE\_ON\_CHAIN\_EVENT | 9 | |
| HUB\_EVENT\_TYPE\_MERGE\_FAILURE | 10 | |
| HUB\_EVENT\_TYPE\_BLOCK\_CONFIRMED | 11 | |
### MergeMessageBody
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------------- | ------------------- | -------- | ----------- |
| message | [Message](#Message) | | |
| deleted\_messages | [Message](#Message) | repeated | |
### MergeUserNameProofBody
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| --------------------------------- | ------------------------------- | ----- | ----------- |
| username\_proof | [UserNameProof](#UserNameProof) | | |
| deleted\_username\_proof | [UserNameProof](#UserNameProof) | | |
| username\_proof\_message | [Message](#Message) | | |
| deleted\_username\_proof\_message | [Message](#Message) | | |
### PruneMessageBody
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------- | ------------------- | ----- | ----------- |
| message | [Message](#Message) | | |
### RevokeMessageBody
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------- | ------------------- | ----- | ----------- |
| message | [Message](#Message) | | |
### MergeOnChainEventBody
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ---------------- | ----------------------------- | ----- | ----------- |
| on\_chain\_event | [OnChainEvent](#OnChainEvent) | | |
### OnChainEvent
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----- | ------------------------------------ |
| type | [OnChainEventType](#OnChainEventType) | | The type of onchain event |
| chain\_id | [uint32](#) | | The chain id for the event |
| block\_number | [uint32](#) | | The block number for the event |
| block\_hash | [bytes](#) | | The block hash for the event |
| block\_timestamp | [uint64](#) | | The block timestamp for the event |
| transaction\_hash | [bytes](#) | | The transaction hash for the event |
| log\_index | [uint32](#) | | The log index for the event |
| fid | [uint64](#) | | The fid the event is associated with |
| body | [SignerEventBody](#signereventbody),
[SignerMigratedEventBody](#signermigratedeventbody),
[IdRegisterEventBody](#idregistereventbody),
[StorageRentEventBody](#storagerenteventbody),
[TierPurchaseBody](#tierpurchasebody) | oneOf | |
| tx\_index | [uint32](#) | | The tx index for the event |
### OnChainEventType
| Name | Number | Description |
| ----------------------------- | ------ | ----------- |
| EVENT\_TYPE\_NONE | 0 | |
| EVENT\_TYPE\_SIGNER | 1 | |
| EVENT\_TYPE\_SIGNER\_MIGRATED | 2 | |
| EVENT\_TYPE\_ID\_REGISTER | 3 | |
| EVENT\_TYPE\_STORAGE\_RENT | 4 | |
| EVENT\_TYPE\_TIER\_PURCHASE | 5 | |
### SignerEventBody
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| -------------- | ----------------------------------- | ----- | -------------------------------------------------- |
| key | [bytes](#) | | The bytes of the public key for the signer |
| key\_type | [uint32](#) | | The type of the key (currently only set to 1) |
| event\_type | [SignerEventType](#SignerEventType) | | The type of the signer event |
| metadata | [bytes](#) | | The metadata associated with the key |
| metadata\_type | [uint32](#) | | The type of the metadata (currently only set to 1) |
### SignerEventType
| Name | Number | Description |
| --------------------------------- | ------ | ----------- |
| SIGNER\_EVENT\_TYPE\_NONE | 0 | |
| SIGNER\_EVENT\_TYPE\_ADD | 1 | |
| SIGNER\_EVENT\_TYPE\_REMOVE | 2 | |
| SIGNER\_EVENT\_TYPE\_ADMIN\_RESET | 3 | |
### SignerMigratedEventBody
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ---------- | ----------- | ----- | -------------------------------------------------------- |
| migratedAt | [uint32](#) | | The timestamp at which nodes were migrated to OP mainnet |
### IdRegisterEventBody
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------------- | ------------------------------------------- | ----- | ------------------------------------------------- |
| to | [bytes](#) | | The address the fid was registered/transferred to |
| event\_type | [IdRegisterEventType](#IdRegisterEventType) | | The type of the id register event |
| from | [bytes](#) | | The address the transfer originated from |
| recovery\_address | [bytes](#) | | The recovery address for the fid |
### IdRegisterEventType
| Name | Number | Description |
| ------------------------------------------- | ------ | ----------- |
| ID\_REGISTER\_EVENT\_TYPE\_NONE | 0 | |
| ID\_REGISTER\_EVENT\_TYPE\_REGISTER | 1 | |
| ID\_REGISTER\_EVENT\_TYPE\_TRANSFER | 2 | |
| ID\_REGISTER\_EVENT\_TYPE\_CHANGE\_RECOVERY | 3 | |
### StorageRentEventBody
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------ | ----------- | ----- | --------------------------------------------------------- |
| payer | [bytes](#) | | The address of the payer |
| units | [uint32](#) | | The number of units of storage purchased |
| expiry | [uint32](#) | | The timestamp at which these units of storage will expire |
### TierPurchaseBody
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| --------- | ----------- | ----- | ----------------------------------- |
| purchaser | [bytes](#) | | The address of the purchaser |
| tier | [uint32](#) | | The tier number purchased |
| units | [uint32](#) | | The number of units purchased |
| expiry | [uint32](#) | | The timestamp at which tier expires |
### MergeFailureBody
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------- | ------------------- | ----- | -------------------------------- |
| message | [Message](#Message) | | The message that failed to merge |
| error | [string](#string) | | The reason for the merge failure |
### BlockConfirmedBody
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------------- | ----------------- | ----- | ---------------------------------------- |
| block\_number | [uint64](#uint64) | | The block number that has been confirmed |
| block\_hash | [bytes](#bytes) | | The hash of the confirmed block |
| shard\_index | [uint32](#uint32) | | The shard index of the confirmed block |
## Messages
A message is the fundamental data type in the Farcaster network.
When an account takes an action like casting a public message, change its profile or verifying an Ethereum account, it
generates a new messages
### 1. Message
The message is a protobuf that contains the data, its hash and a signature from the author.
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------------- | ----------------------------------- | ----- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| data | [MessageData](#MessageData) | | Contents of the message. Alternatively, you can use the data\_bytes to serialize the `MessageData` |
| hash | bytes | | Hash digest of data |
| hash\_scheme | [HashScheme](#HashScheme) | | Hash scheme that produced the hash digest |
| signature | bytes | | Signature of the hash digest |
| signature\_scheme | [SignatureScheme](#SignatureScheme) | | Signature scheme that produced the signature |
| signer | bytes | | Public key or address of the key pair that produced the signature |
| data\_bytes | bytes | | Alternate to the "data" field. If you are constructing the [MessageData](#MessageData) in a programming language other than Typescript, you can use this field to serialize the `MessageData` and calculate the `hash` and `signature` on these bytes. Optional. |
#### 1.1 MessageData
MessageData is a generic envelope that contains a type, fid, timestamp and network which must be present in all
Farcaster messages. It also contains a body whose type is determined by the MessageType.
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| --------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----- | ---------------------------------------------- |
| type | [MessageType](#MessageType) | | Type of Message contained in the body |
| fid | uint64 | | Farcaster ID of the user producing the message |
| timestamp | uint32 | | Farcaster epoch timestamp in seconds |
| network | [FarcasterNetwork](#FarcasterNetwork) | | Farcaster network the message is intended for |
| body | [CastAddBody](#CastAddBody),
[CastRemoveBody](#CastRemoveBody),
[ReactionBody](#ReactionBody),
[VerificationAddAddressBody](#VerificationAddAddressBody),
[VerificationRemoveBody](#VerificationRemoveBody),
[UserDataBody](#UserDataBody),
[LinkBody](#LinkBody),
[UserNameProof](#UserNameProof),
[FrameActionBody](#FrameActionBody),
[LinkCompactStateBody](#LinkCompactStateBody) | oneOf | Properties specific to the MessageType |
#### 1.2 HashScheme
Type of hashing scheme used to produce a digest of MessageData
| Name | Number | Description |
| -------------------- | ------ | -------------------------------------- |
| HASH\_SCHEME\_NONE | 0 | |
| HASH\_SCHEME\_BLAKE3 | 1 | Default scheme for hashing MessageData |
#### 1.3 Signature Scheme
Type of signature scheme used to sign the Message hash
| Name | Number | Description |
| -------------------------- | ------ | ------------------------------------ |
| SIGNATURE\_SCHEME\_NONE | 0 | |
| SIGNATURE\_SCHEME\_ED25519 | 1 | Ed25519 signature (default) |
| SIGNATURE\_SCHEME\_EIP712 | 2 | ECDSA signature using EIP-712 scheme |
#### 1.4 Message Type
Type of the MessageBody
| Name | Number | Description |
| ---------------------------------------------- | ------ | -------------------------------- |
| MESSAGE\_TYPE\_NONE | 0 | Invalid default value |
| MESSAGE\_TYPE\_CAST\_ADD | 1 | Add a new Cast |
| MESSAGE\_TYPE\_CAST\_REMOVE | 2 | Remove an existing Cast |
| MESSAGE\_TYPE\_REACTION\_ADD | 3 | Add a Reaction to a Cast |
| MESSAGE\_TYPE\_REACTION\_REMOVE | 4 | Remove a Reaction from a Cast |
| MESSAGE\_TYPE\_LINK\_ADD | 5 | Add a Link to a target |
| MESSAGE\_TYPE\_LINK\_REMOVE | 6 | Remove a Link from a target |
| MESSAGE\_TYPE\_VERIFICATION\_ADD\_ETH\_ADDRESS | 7 | Add a Verification of an Address |
| MESSAGE\_TYPE\_VERIFICATION\_REMOVE | 8 | Remove a Verification |
| MESSAGE\_TYPE\_USER\_DATA\_ADD | 11 | Add metadata about a user |
| MESSAGE\_TYPE\_USERNAME\_PROOF | 12 | Add or replace a username proof |
| MESSAGE\_TYPE\_FRAME\_ACTION | 13 | Frame action (not stored) |
| MESSAGE\_TYPE\_LINK\_COMPACT\_STATE | 14 | Compact state for links |
#### 1.5 Farcaster Network
Farcaster network the message is intended for
| Name | Number | Description |
| --------------------------- | ------ | ---------------------- |
| FARCASTER\_NETWORK\_NONE | 0 | |
| FARCASTER\_NETWORK\_MAINNET | 1 | Public primary network |
| FARCASTER\_NETWORK\_TESTNET | 2 | Public test network |
| FARCASTER\_NETWORK\_DEVNET | 3 | Private test network |
### 2. UserData
A UserData message represents user metadata (e.g. a profile picture url) .
#### 2.1 UserDataBody
Body of a UserData message
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----- | ----------------------------- | ----- | --------------------- |
| type | [UserDataType](#UserDataType) | | Type of metadata |
| value | string | | Value of the metadata |
#### 2.2 UserDataType
Type of UserData message
| Name | Number | Description |
| -------------------------------------- | ------ | ------------------------------------- |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_NONE | 0 | Invalid default value |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_PFP | 1 | Profile Picture for the user |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_DISPLAY | 2 | Display Name for the user |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_BIO | 3 | Bio for the user |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_URL | 5 | URL of the user |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_USERNAME | 6 | Preferred Farcaster Name for the user |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_LOCATION | 7 | Location for the user |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_TWITTER | 8 | Twitter username for the user |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_GITHUB | 9 | GitHub username for the user |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_BANNER | 10 | Banner image for the user |
| USER\_DATA\_PRIMARY\_ADDRESS\_ETHEREUM | 11 | Primary Ethereum address |
| USER\_DATA\_PRIMARY\_ADDRESS\_SOLANA | 12 | Primary Solana address |
See [FIP-196](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/protocol/discussions/196) for more information on Location.
See [FIP-19](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/protocol/discussions/199) for more information on Twitter/X and Github usernames.
### 3. Cast
A Cast message is a public post from a user.
#### 3.1 CastAddBody
Adds a new Cast message.
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------------------- | --------------------- | ------------ | ------------------------------------------- |
| embeds\_deprecated | string | repeated | URLs to be embedded in the cast |
| mentions | uint64 | repeated | Fids mentioned in the cast |
| parent\_cast\_id | [CastId](#CastId) | oneOf parent | Parent cast of the cast |
| parent\_url | string | oneOf parent | Parent URL of the cast |
| text | string | | Text of the cast |
| mentions\_positions | uint32 | repeated | Positions of the mentions in the text |
| embeds | [Embed](#Embed) | repeated | URLs or cast ids to be embedded in the cast |
| type | [CastType](#CastType) | | Type of cast (regular, long, etc.) |
##### Embed
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| -------- | ----------------- | ----- | ----------- |
| url | [string](#string) | | |
| cast\_id | [CastId](#CastId) | | |
#### 3.2 CastRemoveBody
Removes an existing Cast message.
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------------ | ----- | ----- | -------------------------- |
| target\_hash | bytes | | Hash of the cast to remove |
#### 3.3 CastId
Identifier used to look up a Cast
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----- | ------ | ----- | ------------------------------------ |
| fid | uint64 | | Fid of the user who created the cast |
| hash | bytes | | Hash of the cast |
### 4. Reaction
A Reaction message creates a relationship between an account and a cast. (e.g. like)
#### 4.1 ReactionBody
Adds or removes a Reaction from a Cast
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ---------------- | ----------------------------- | ----- | ------------------------------ |
| type | [ReactionType](#ReactionType) | | Type of reaction |
| target\_cast\_id | [CastId](#CastId) | | CastId of the Cast to react to |
| target\_url | [string](#string) | | URL to react to |
#### 4.2 ReactionType
Type of Reaction
| Name | Number | Description |
| ---------------------- | ------ | ---------------------------------------- |
| REACTION\_TYPE\_NONE | 0 | Invalid default value |
| REACTION\_TYPE\_LIKE | 1 | Like the target cast |
| REACTION\_TYPE\_RECAST | 2 | Share target cast to the user's audience |
### 5. Link
A Link message creates a relationship between two users (e.g. follow)
#### 5.1 LinkBody
Adds or removes a Link
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ---------------- | ----------------- | -------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| type | [string](#string) | | Type of link, \<= 8 characters |
| displayTimestamp | [uint32](#uint32) | optional | User-defined timestamp that preserves original timestamp when message.data.timestamp needs to be updated for compaction |
| target\_fid | [uint64](#uint64) | | The fid the link relates to |
### 6. Verification
A Verification message is a proof of ownership of something.
#### 6.1 VerificationAddAddressBody
Adds a bi-directional signature proving that an fid has control over an address (supports multiple protocols).
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------------------ | --------------------- | ----- | ---------------------------------------------------- |
| address | bytes | | Address being verified |
| claim\_signature | bytes | | Signature produced by the user's address |
| block\_hash | bytes | | Hash of the latest block when the claim was produced |
| verification\_type | uint32 | | Type of verification (0 = EOA, 1 = contract) |
| chain\_id | uint32 | | Chain ID of the verification |
| protocol | [Protocol](#Protocol) | | Protocol of the address (Ethereum, Solana, etc.) |
#### 6.2 VerificationRemoveBody
Removes a Verification of any type
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------- | ----- | ----- | ------------------------------------- |
| address | bytes | | Address of the Verification to remove |
### 7. Frame Action
Represents an action performed by a user on a frame. This message is not stored on the nodes and cannot be submitted,
only validated.
#### 7.1 FrameActionBody
A user action on a frame
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| --------------- | ----------------- | ----- | ----------------------------------------------------- |
| url | bytes | | The original url of the frame as embedded in the cast |
| button\_index | uint32 | | The button that was pressed (indexed from 1) |
| cast\_id | [CastId](#CastId) | | The cast id that hosted the frame |
| input\_text | bytes | | Any text the user input as part of the action |
| state | bytes | | Serialized state passed from frame to server |
| transaction\_id | bytes | | Transaction ID for transaction frames |
| address | bytes | | Address involved in the frame action |
### 8. Protocol
Type of protocol for addresses
| Name | Number | Description |
| ------------------ | ------ | ----------- |
| PROTOCOL\_ETHEREUM | 0 | Ethereum |
| PROTOCOL\_SOLANA | 1 | Solana |
### 9. CastType
Type of cast
| Name | Number | Description |
| ------------ | ------ | --------------------------- |
| CAST | 0 | Regular cast |
| LONG\_CAST | 1 | Extended length cast |
| TEN\_K\_CAST | 2 | Ten thousand character cast |
### 10. LinkCompactStateBody
Compact state representation for links
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------------ | ----------------- | -------- | -------------------- |
| type | [string](#string) | | Type of link |
| target\_fids | [uint64](#uint64) | repeated | Array of target fids |
## Casts API
### castById
Get a cast by its FID and Hash.
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | ----------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------- |
| fid | The FID of the cast's creator | `fid=6833` |
| hash | The cast's hash | `hash=0xa48dd46161d8e57725f5e26e34ec19c13ff7f3b9` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/castById?fid=2&hash=0xd2b1ddc6c88e865a33cb1a565e0058d757042974
```
**Response**
```json
{
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_CAST_ADD",
"fid": 2,
"timestamp": 48994466,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"castAddBody": {
"embedsDeprecated": [],
"mentions": [],
"parentCastId": {
"fid": 226,
"hash": "0xa48dd46161d8e57725f5e26e34ec19c13ff7f3b9"
},
"text": "Cast Text",
"mentionsPositions": [],
"embeds": []
}
},
"hash": "0xd2b1ddc6c88e865a33cb1a565e0058d757042974",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "3msLXzxB4eEYe...dHrY1vkxcPAA==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x78ff9a...58c"
}
```
### castsByFid
Fetch all casts for authored by an FID.
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| -------------- | ---------------------------------- | --------------------------- |
| fid | The FID of the cast's creator | `fid=6833` |
| pageSize | Optional page size (default: 1000) | `pageSize=100` |
| pageToken | Optional page token for pagination | `pageToken=DAEDAAAGlQ...` |
| reverse | Optional reverse order flag | `reverse=true` |
| startTimestamp | Optional start timestamp filter | `startTimestamp=1640995200` |
| stopTimestamp | Optional stop timestamp filter | `stopTimestamp=1640995200` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/castsByFid?fid=2
```
**Response**
```json
{
"messages": [
{
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_CAST_ADD",
"fid": 2,
"timestamp": 48994466,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"castAddBody": {... },
"text": "Cast Text",
"mentionsPositions": [],
"embeds": []
}
},
"hash": "0xd2b1ddc6c88e865a33cb1a565e0058d757042974",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "3msLXzxB4eEYeF0Le...dHrY1vkxcPAA==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x78ff9a768cf1...2eca647b6d62558c"
}
]
"nextPageToken": ""
}
```
### castsByParent
Fetch all casts by parent cast's FID and Hash OR by the parent's URL
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | ---------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| fid | The FID of the parent cast | `fid=6833` |
| hash | The parent cast's hash | `hash=0xa48dd46161d8e57725f5e26e34ec19c13ff7f3b9` |
| url | The URL of the parent cast | `url=chain://eip155:1/erc721:0x39d89b649ffa044383333d297e325d42d31329b2` |
| pageSize | Optional page size (default: 1000) | `pageSize=100` |
| pageToken | Optional page token for pagination | `pageToken=DAEDAAAGlQ...` |
| reverse | Optional reverse order flag | `reverse=true` |
**Note**
You can use either `?fid=...&hash=...` OR `?url=...` to query this endpoint
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/castsByParent?fid=226&hash=0xa48dd46161d8e57725f5e26e34ec19c13ff7f3b9
```
**Response**
```json
{
"messages": [
{
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_CAST_ADD",
"fid": 226,
"timestamp": 48989255,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"castAddBody": {
"embedsDeprecated": [],
"mentions": [],
"parentCastId": {
"fid": 226,
"hash": "0xa48dd46161d8e57725f5e26e34ec19c13ff7f3b9"
},
"text": "Cast's Text",
"mentionsPositions": [],
"embeds": []
}
},
"hash": "0x0e501b359f88dcbcddac50a8f189260a9d02ad34",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "MjKnOQCTW42K8+A...tRbJfia2JJBg==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x6f1e8758...7f04a3b500ba"
}
],
"nextPageToken": ""
}
```
### castsByMention
Fetch all casts that mention an FID
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | ----------------------------------- | ------------------------- |
| fid | The FID that is mentioned in a cast | `fid=6833` |
| pageSize | Optional page size (default: 1000) | `pageSize=100` |
| pageToken | Optional page token for pagination | `pageToken=DAEDAAAGlQ...` |
| reverse | Optional reverse order flag | `reverse=true` |
**Note**
Use the `mentionsPositions` to extract the offset in the cast text where the FID was mentioned
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/castsByMention?fid=6833
```
**Response**
```json
{
"messages": [
{
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_CAST_ADD",
"fid": 2,
"timestamp": 62298143,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"castAddBody": {
"embedsDeprecated": [],
"mentions": [15, 6833],
"parentCastId": {
"fid": 2,
"hash": "0xd5540928cd3daf2758e501a61663427e41dcc09a"
},
"text": "cc and ",
"mentionsPositions": [3, 8],
"embeds": []
}
},
"hash": "0xc6d4607835197a8ee225e9218d41e38aafb12076",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "TOaWrSTmz+cyzPMFGvF...OeUznB0Ag==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x78ff9a768c...647b6d62558c"
}
],
"nextPageToken": ""
}
```
## Events API
The events API returns events as they are merged into the Hub, which can be used to listen to Hub activity.
### eventById
Get an event by its Id
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| ------------ | ----------------------------- | -------------------------- |
| event\_id | The Hub Id of the event | `event_id=350909155450880` |
| shard\_index | The shard index for the event | `shard_index=1` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/eventById?event_id=151622205440&shard_index=1
```
**Response**
```json
{
"type": "HUB_EVENT_TYPE_BLOCK_CONFIRMED",
"id": 151622205440,
"blockConfirmedBody": {
"blockNumber": 9254285,
"shardIndex": 1,
"timestamp": 142732801,
"blockHash": "0x95659381b61ac3cd9fc06e61d9d9c256f8274aaab526cb23ce72856c2017f721",
"totalEvents": 10
},
"blockNumber": 9254285,
"shardIndex": 1
}
```
### events
Get a page of Hub events
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------- |
| from\_event\_id | An optional Hub Id to start getting events from. Set it to `0` to start from the first event | `from_event_id=350909155450880` |
| shard\_index | Optional shard index to query | `shard_index=1` |
| stop\_id | Optional stop event ID | `stop_id=350909170294785` |
| pageSize | Optional page size (default: 1000) | `pageSize=100` |
| pageToken | Optional page token for pagination | `pageToken=DAEDAAAGlQ...` |
| reverse | Optional reverse order flag | `reverse=true` |
**Note**
Hubs prune events older than 3 days, so not all historical events can be fetched via this API
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/events?from_event_id=0
```
**Response**
```json
{
"events": [
{
"type": "HUB_EVENT_TYPE_BLOCK_CONFIRMED",
"id": 151622205440,
"blockConfirmedBody": {
"blockNumber": 9254285,
"shardIndex": 1,
"timestamp": 142732801,
"blockHash": "0x95659381b61ac3cd9fc06e61d9d9c256f8274aaab526cb23ce72856c2017f721",
"totalEvents": 10
},
"blockNumber": 9254285,
"shardIndex": 1
},
{
"type": "HUB_EVENT_TYPE_MERGE_MESSAGE",
"id": 151622205441,
"mergeMessageBody": {
"message": {
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_REACTION_ADD",
"fid": 310826,
"timestamp": 142732800,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"reactionBody": {
"type": "REACTION_TYPE_LIKE",
"targetCastId": {
"fid": 1026688,
"hash": "0xa1162b5d59281733daee1bcd3b810c5259f66ee1"
}
}
},
"hash": "0xfd4e55bb235fec5cad679182a2c926948d95b7cb",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "3N0jZHh46/gXa6uZS+jCbw/9eiOti3MyHNODn7cw5xqo7DBa45rixbzG2QNJtnDmF5XJb+q4GNv/eZF+19qQBw==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x217a69e523fbcc51643021d78f9a0fc98ac4e56c7418a2825f0870c81a5d18aa"
},
"deletedMessages": []
},
"blockNumber": 9254285,
"shardIndex": 1
}
]
}
```
## Fids API
### fids
Get a list of all the FIDs
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | ---------------------------------- | ------------------------- |
| shard\_id | Required shard ID to query | `shard_id=1` |
| pageSize | Optional page size (default: 1000) | `pageSize=100` |
| pageToken | Optional page token for pagination | `pageToken=DAEDAAAGlQ...` |
| reverse | Optional reverse order flag | `reverse=true` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/fids?shard_id=1
```
**Response**
```json
{
"fids": [1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 12, 15, 17, 18, 19, 21, 22, 23, 30, 31, 33, 36, 37, 41, 43, 47, 48, 52, 54, 55, 57, 58, 60, 62, 65, 67, 68, 70, 77, 79, 81, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 99, 106],
"nextPageToken": "DAEDAAAGlQarXegAAACK"
}
```
## HTTP API
Snapchain nodes serve a HTTP API on port 3381 by default.
### Using the API
The API can be called from any programming language or browser by making a normal HTTP request.
**View the API responses in a browser**
Simply open the URL in a browser
[http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/castsByFid?fid=2](http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/castsByFid?fid=2)
**Call the API using curl**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/castsByFid?fid=2
```
**Call the API via Javascript, using the axios library**
```javascript
import axios from "axios";
const fid = 2;
const server = "http://127.0.0.1:3381";
try {
const response = await axios.get(`${server}/v1/castsByFid?fid=${fid}`);
console.log(`API Returned HTTP status ${response.status}`);
console.log(`First Cast's text is ${response.messages[0].data.castAddBody.text}`);
} catch (e) {
// Handle errors
console.log(response);
}
```
### Response encoding
Responses from the API are encoded as `application/json`, and can be parsed as normal JSON objects.
1. Hashes, ETH addresses, keys etc... are all encoded as hex strings starting with `0x`
2. Signatures and other binary fields are encoded in base64
3. Constants are encoded as their string types. For example, the `hashScheme` is encoded as `HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3` which is equivalent to the `HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3 = 1` from the protobuf schema.
### Timestamps
Messages contain timestamps which are seconds since the Farcaster Epoch, which began on Jan 1, 2021 00:00:00 UTC.
### Paging
Most endpoints support paging to get a large number of responses.
**Pagination Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | ----------------------------------- |
| pageSize | Maximum number of messages to return in a single response | `pageSize=100` |
| reverse | Reverse the sort order, returning latest messages first | `reverse=1` |
| pageToken | The page token returned by the previous query, to fetch the next page. If this parameters is empty, fetch the first page | `pageToken=AuzO1V0Dta...fStlynsGWT` |
The returned `nextPageToken` is empty if there are no more pages to return.
Pagination query parameters can be combined with other query parameters supported by the endpoint. For example, `/v1/casts?fid=2&pageSize=3`.
**Example**
Fetch all casts by FID `2`, fetching upto 3 casts per Page
```bash
# Fetch first page
http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/castsByFid?fid=2&pageSize=3
# Fetch next page. The pageToken is from the previous response(`response.nextPageToken`)
http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/castsByFid?fid=2&pageSize=3&pageToken=AuzO1V0DtaItCwwa10X6YsfStlynsGWT
```
**Javascript Example**
```javascript
import axios from "axios";
const fid = 2;
const server = "http://127.0.0.1:3381";
let nextPageToken = "";
do {
const response = await axios.get(`${server}/v1/castsByFid?fid=${fid}&pageSize=100&nextPageToken=${nextPageToken}`);
// Process response....
nextPageToken = response.nextPageToken;
} while (nextPageToken !== "")
```
### Timestamp Filtering
Some endpoints support filtering by timestamp, allowing you to retrieve results within a specific time range:
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| -------------- | ----------------------------------- | --------------------- |
| startTimestamp | Start of the time range (inclusive) | `startTimestamp=1000` |
| stopTimestamp | End of the time range (inclusive) | `stopTimestamp=2000` |
Example:
```bash
# Get casts from FID 2 between timestamps 1000 and 2000
http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/castsByFid?fid=2&startTimestamp=1000&stopTimestamp=2000
```
### Handling Errors
If there's an API error, the HTTP status code is set to `400` or `500` as appropriate. The response is a JSON object with `detail`, `errCode` and `metadata` fields set to identify and debug the errors.
**Example**
```bash
$ curl "http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/castById?fid=invalid"
{
"errCode": "bad_request.validation_failure",
"presentable": false,
"name": "HubError",
"code": 3,
"details": "fid must be an integer",
"metadata": {
"errcode": [
"bad_request.validation_failure",
],
},
}
```
### Limitations
The HTTP API currently does not support any of the Sync APIs that are available in the gRPC version. When nodes sync with each other, they will use the gRPC APIs instead of the HTTP APIs.
## Info API
### info
Get the Hub's info
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | -------------------------- | ----------- |
| dbstats | Whether to return DB stats | `dbstats=1` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/info?dbstats=1
```
**Response**
```json
{
"version": "1.5.5",
"isSyncing": false,
"nickname": "Farcaster Hub",
"rootHash": "fa349603a6c29d27041225261891bc9bc846bccb",
"dbStats": {
"numMessages": 4191203,
"numFidEvents": 20287,
"numFnameEvents": 20179
},
"peerId": "12D3KooWNr294AH1fviDQxRmQ4K79iFSGoRCWzGspVxPprJUKN47",
"hubOperatorFid": 6833
}
```
## Links API
A Link represents a relationship between two users (e.g. follow)
The Links API will accept the following values for the `link_type` field.
| String | Description |
| ------ | ----------------------------- |
| follow | Follow from FID to Target FID |
### linkById
Get a link by its FID and target FID.
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| ----------- | ----------------------------------- | ------------------ |
| fid | The FID of the link's originator | `fid=6833` |
| target\_fid | The FID of the target of the link | `target_fid=2` |
| link\_type | The type of link, as a string value | `link_type=follow` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/linkById?fid=6833&target_fid=2&link_type=follow
```
**Response**
```json
{
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_LINK_ADD",
"fid": 6833,
"timestamp": 61144470,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"linkBody": {
"type": "follow",
"targetFid": 2
}
},
"hash": "0x58c23eaf4f6e597bf3af44303a041afe9732971b",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "sMypYEMqSyY...nfCA==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x0852c07b56...06e999cdd"
}
```
### linksByFid
Get all links from a source FID
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| ---------- | ----------------------------------- | ------------------------- |
| fid | The FID of the link's creator | `fid=6833` |
| link\_type | The type of link, as a string value | `link_type=follow` |
| pageSize | Optional page size (default: 1000) | `pageSize=100` |
| pageToken | Optional page token for pagination | `pageToken=DAEDAAAGlQ...` |
| reverse | Optional reverse order flag | `reverse=true` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/linksByFid?fid=6833
```
**Response**
```json
{
"messages": [
{
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_LINK_ADD",
"fid": 6833,
"timestamp": 61144470,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"linkBody": {
"type": "follow",
"targetFid": 83
}
},
"hash": "0x094e35891519c0e04791a6ba4d2eb63d17462f02",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "qYsfX08mS...McYq6IYMl+ECw==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x0852c0...a06e999cdd"
}
],
"nextPageToken": ""
}
```
### linksByTargetFid
Get all links to a target FID
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| ----------- | ----------------------------------- | ------------------------- |
| target\_fid | The FID of the link's target | `target_fid=6833` |
| link\_type | The type of link, as a string value | `link_type=follow` |
| pageSize | Optional page size (default: 1000) | `pageSize=100` |
| pageToken | Optional page token for pagination | `pageToken=DAEDAAAGlQ...` |
| reverse | Optional reverse order flag | `reverse=true` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/linksByTargetFid?target_fid=6833
```
**Response**
```json
{
"messages": [
{
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_LINK_ADD",
"fid": 302,
"timestamp": 61144668,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"linkBody": {
"type": "follow",
"targetFid": 6833
}
},
"hash": "0x78c62531d96088f640ffe7e62088b49749efe286",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "frIZJGIizv...qQd9QJyCg==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x59a04...6860ddfab"
}
],
"nextPageToken": ""
}
```
## Message API
The Message API lets you validate and submit signed Farcaster protocol messages to the Hub. Note that the message has to
be sent as the encoded bytestream of the protobuf (`Message.encode(msg).finish()` in typescript), as POST data to the
endpoint.
The encoding of the POST data has to be set to `application/octet-stream`. The endpoint returns the Message object as
JSON if it was successfully submitted or validated
### submitMessage
Submit a signed protobuf-serialized message to the Hub
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | ----------------------------------- | ------- |
| | This endpoint accepts no parameters | |
**Example**
```bash
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/submitMessage" \
-H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" \
--data-binary "@message.encoded.protobuf"
```
**Response**
```json
{
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_CAST_ADD",
"fid": 2,
"timestamp": 48994466,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"castAddBody": {
"embedsDeprecated": [],
"mentions": [],
"parentCastId": {
"fid": 226,
"hash": "0xa48dd46161d8e57725f5e26e34ec19c13ff7f3b9"
},
"text": "Cast Text",
"mentionsPositions": [],
"embeds": []
}
},
"hash": "0xd2b1ddc6c88e865a33cb1a565e0058d757042974",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "3msLXzxB4eEYe...dHrY1vkxcPAA==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x78ff9a...58c"
}
```
### submitBulkMessages
Submit several signed protobuf-serialized messages to the Hub at once. Each one will be submitted to the node sequentially.
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | ----------------------------------- | ------- |
| | This endpoint accepts no parameters | |
**Example**
```bash
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/submitBulkMessages" \
-H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" \
--data-binary "@SubmitBulkMessagesRequest.encoded.protobuf"
```
**Response**
```json
[
{
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_CAST_ADD",
"fid": 2,
"timestamp": 48994466,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"castAddBody": {
"embedsDeprecated": [],
"mentions": [],
"parentCastId": {
"fid": 226,
"hash": "0xa48dd46161d8e57725f5e26e34ec19c13ff7f3b9"
},
"text": "Cast Text",
"mentionsPositions": [],
"embeds": []
}
},
"hash": "0xd2b1ddc6c88e865a33cb1a565e0058d757042974",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "3msLXzxB4eEYe...dHrY1vkxcPAA==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x78ff9a...58c"
},
{ // ....
}
]
```
#### Auth
If the rpc auth has been enabled on the server (using `--rpc-auth username:password`), you will need to also pass in the
username and password while calling `submitMessage` or `submitBulkMessages` using HTTP Basic Auth.
**Example**
```bash
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/submitMessage" \
-u "username:password" \
-H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" \
--data-binary "@message.encoded.protobuf"
```
**JS Example**
```Javascript
import axios from "axios";
const url = `http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/submitMessage`;
const postConfig = {
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/octet-stream" },
auth: { username: "username", password: "password" },
};
// Encode the message into a Buffer (of bytes)
const messageBytes = Buffer.from(Message.encode(castAdd).finish());
try {
const response = await axios.post(url, messageBytes, postConfig);
} catch (e) {
// handle errors...
}
```
### validateMessage
Validate a signed protobuf-serialized message with the Hub. This can be used to verify that the hub will consider the
message valid. Or to validate message that cannot be submitted (e.g. Frame actions)
\::: details
The hub validates the following for all messages:
* The fid is registered
* The signer is active and registered to the fid
* The message hash is correct
* The signature is valid and corresponds to the signer
* Any other message specific validation
For FrameAction messages, note that the hub does not validate the castId is actually an existing cast. Nor
does it validate the frame url matches the embedded url in the cast. Make sure to check for this if it's
important for your application.
\:::
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | ----------------------------------- | ------- |
| | This endpoint accepts no parameters | |
**Example**
```bash
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/validateMessage" \
-H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" \
--data-binary "@message.encoded.protobuf"
```
**Response**
```json
{
"valid": true,
"message": {
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_FRAME_ACTION",
"fid": 2,
"timestamp": 48994466,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"frameActionBody": {
"url": "https://fcpolls.com/polls/1",
"buttonIndex": 2,
"inputText": "",
"castId": {
"fid": 226,
"hash": "0xa48dd46161d8e57725f5e26e34ec19c13ff7f3b9"
}
}
},
"hash": "0xd2b1ddc6c88e865a33cb1a565e0058d757042974",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "3msLXzxB4eEYe...dHrY1vkxcPAA==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x78ff9a...58c"
}
}
```
### Using with Rust, Go or other programming languages
Messages need to be signed with a Ed25519 account key belonging to the FID. If you are using a different programming
language
than Typescript, you can manually construct the `MessageData` object and serialize it to the `data_bytes` field of the
message. Then, use the `data_bytes` to compute the `hash` and `signature`. Please see
the [`rust-submitmessage` example](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/hub-monorepo/tree/main/packages/hub-web/examples) for
more details
```rust
use ed25519_dalek::{SecretKey, Signer, SigningKey};
use hex::FromHex;
use reqwest::Client;
use message::{CastAddBody, FarcasterNetwork, MessageData};
use protobuf::Message;
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() {
let fid = 6833; // FID of the user submitting the message
let network = FarcasterNetwork::FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET;
// Construct the cast add message
let mut cast_add = CastAddBody::new();
cast_add.set_text("Welcome to Rust!".to_string());
// Construct the cast add message data object
let mut msg_data = MessageData::new();
msg_data.set_field_type(message::MessageType::MESSAGE_TYPE_CAST_ADD);
msg_data.set_fid(fid);
msg_data.set_timestamp(
(std::time::SystemTime::now()
.duration_since(FARCASTER_EPOCH)
.unwrap()
.as_secs()) as u32,
);
msg_data.set_network(network);
msg_data.set_cast_add_body(cast_add);
let msg_data_bytes = msg_data.write_to_bytes().unwrap();
// Calculate the blake3 hash, trucated to 20 bytes
let hash = blake3::hash(&msg_data_bytes).as_bytes()[0..20].to_vec();
// Construct the actual message
let mut msg = message::Message::new();
msg.set_hash_scheme(message::HashScheme::HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3);
msg.set_hash(hash);
// Sign the message. You need to use a signing key that corresponds to the FID you are adding.
// REPLACE THE PRIVATE KEY WITH YOUR OWN
let private_key = SigningKey::from_bytes(
&SecretKey::from_hex("0x...").expect("Please provide a valid private key"),
);
let signature = private_key.sign(&msg_data_bytes).to_bytes();
msg.set_signature_scheme(message::SignatureScheme::SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519);
msg.set_signature(signature.to_vec());
msg.set_signer(private_key.verifying_key().to_bytes().to_vec());
// Serialize the message
msg.set_data_bytes(msg_data_bytes.to_vec());
let msg_bytes = msg.write_to_bytes().unwrap();
// Finally, submit the message to the network
// Create a reqwest Client
let client = Client::new();
// Define your endpoint URL
let url = "http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/submitMessage";
// Make the POST request
let res = client
.post(url)
.header("Content-Type", "application/octet-stream")
.body(msg_bytes)
.send()
.await
.unwrap();
// Check if it's success
if res.status().is_success() {
println!("Successfully sent the message.");
} else {
println!("Failed to send the message. HTTP status: {}", res.status());
}
}
```
## On Chain API
### onChainSignersByFid
Get a list of account keys (signers) provided by an FID
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | ---------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| fid | The FID being requested | `fid=2` |
| signer | The optional key of signer | `signer=0x0852c07b5695ff94138b025e3f9b4788e06133f04e254f0ea0eb85a06e999cdd` |
| pageSize | Optional page size (default: 1000) | `pageSize=100` |
| pageToken | Optional page token for pagination | `pageToken=DAEDAAAGlQ...` |
| reverse | Optional reverse order flag | `reverse=true` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/onChainSignersByFid?fid=6833
```
**Response**
```json
{
"events": [
{
"type": "EVENT_TYPE_SIGNER",
"chainId": 10,
"blockNumber": 108875854,
"blockHash": "0xceb1cdc21ee319b06f0455f1cedc0cd4669b471d283a5b2550b65aba0e0c1af0",
"blockTimestamp": 1693350485,
"transactionHash": "0x76e20cf2f7c3db4b78f00f6bb9a7b78b0acfb1eca4348c1f4b5819da66eb2bee",
"logIndex": 2,
"fid": 6833,
"signerEventBody": {
"key": "0x0852c07b5695ff94138b025e3f9b4788e06133f04e254f0ea0eb85a06e999cdd",
"keyType": 1,
"eventType": "SIGNER_EVENT_TYPE_ADD",
"metadata": "AAAAAAAAAAAA...AAAAAAAA",
"metadataType": 1
},
"txIndex": 0
}
]
}
```
### onChainEventsByFid
Get a list of account keys provided by an FID
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| ----------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| fid | The FID being requested | `fid=2` |
| event\_type | The string value of the event type being requested. This parameter is required | `event_type=EVENT_TYPE_SIGNER` OR `event_type=EVENT_TYPE_STORAGE_RENT` |
| pageSize | Optional page size (default: 1000) | `pageSize=100` |
| pageToken | Optional page token for pagination | `pageToken=DAEDAAAGlQ...` |
| reverse | Optional reverse order flag | `reverse=true` |
The onChainEventsByFid API will accept the following values for the `event_type` field.
| String |
| ----------------------------- |
| EVENT\_TYPE\_NONE |
| EVENT\_TYPE\_SIGNER |
| EVENT\_TYPE\_SIGNER\_MIGRATED |
| EVENT\_TYPE\_ID\_REGISTER |
| EVENT\_TYPE\_STORAGE\_RENT |
| EVENT\_TYPE\_TIER\_PURCHASE |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/onChainEventsByFid?fid=3&event_type=EVENT_TYPE_SIGNER
```
**Response**
```json
{
"events": [
{
"type": "EVENT_TYPE_SIGNER",
"chainId": 10,
"blockNumber": 108875456,
"blockHash": "0x75fbbb8b2a4ede67ac350e1b0503c6a152c0091bd8e3ef4a6927d58e088eae28",
"blockTimestamp": 1693349689,
"transactionHash": "0x36ef79e6c460e6ae251908be13116ff0065960adb1ae032b4cc65a8352f28952",
"logIndex": 2,
"fid": 3,
"signerEventBody": {
"key": "0xc887f5bf385a4718eaee166481f1832198938cf33e98a82dc81a0b4b81ffe33d",
"keyType": 1,
"eventType": "SIGNER_EVENT_TYPE_ADD",
"metadata": "AAAAAAAAA...AAAAA",
"metadataType": 1
},
"txIndex": 0
}
]
}
```
### onChainIdRegistryEventByAddress
Get a list of on chain events for a given Address
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | ------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------- |
| address | The ETH address being requested | `address=0x74232bf61e994655592747e20bdf6fa9b9476f79` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/onChainIdRegistryEventByAddress?address=0x74232bf61e994655592747e20bdf6fa9b9476f79
```
**Response**
```json
{
"type": "EVENT_TYPE_ID_REGISTER",
"chainId": 10,
"blockNumber": 108874508,
"blockHash": "0x20d83804a26247ad8c26d672f2212b28268d145b8c1cefaa4126f7768f46682e",
"blockTimestamp": 1693347793,
"transactionHash": "0xf3481fc32227fbd982b5f30a87be32a2de1fc5736293cae7c3f169da48c3e764",
"logIndex": 7,
"fid": 3,
"idRegisterEventBody": {
"to": "0x74232bf61e994655592747e20bdf6fa9b9476f79",
"eventType": "ID_REGISTER_EVENT_TYPE_REGISTER",
"from": "0x",
"recoveryAddress": "0x00000000fcd5a8e45785c8a4b9a718c9348e4f18"
},
"txIndex": 0
}
```
### fidAddressType
Get the address type information for a given FID and address
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | ------------------------ | ---------------------------------------------------- |
| fid | The FID being requested | `fid=2` |
| address | The ETH address to check | `address=0x91031dcfdea024b4d51e775486111d2b2a715871` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/fidAddressType?fid=2&address=0x91031dcfdea024b4d51e775486111d2b2a715871
```
**Response**
```json
{
"is_custody": false,
"is_auth": false,
"is_verified": true
}
```
## Reactions API
The Reactions API will accept the following values for the `reaction_type` field.
| String | Description |
| ------ | ---------------------------------------- |
| Like | Like the target cast |
| Recast | Share target cast to the user's audience |
### reactionById
Get a reaction by its created FID and target Cast.
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| -------------- | ----------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------- |
| fid | The FID of the reaction's creator | `fid=6833` |
| target\_fid | The FID of the cast's creator | `target_fid=2` |
| target\_hash | The cast's hash | `target_hash=0xa48dd46161d8e57725f5e26e34ec19c13ff7f3b9` |
| reaction\_type | The type of reaction, use string representation | `reaction_type=Like` OR `reaction_type=Recast` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/reactionById?fid=2&reaction_type=Like&target_fid=1795&target_hash=0x7363f449bfb0e7f01c5a1cc0054768ed5146abc0
```
**Response**
```json
{
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_REACTION_ADD",
"fid": 2,
"timestamp": 72752656,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"reactionBody": {
"type": "REACTION_TYPE_LIKE",
"targetCastId": {
"fid": 1795,
"hash": "0x7363f449bfb0e7f01c5a1cc0054768ed5146abc0"
}
}
},
"hash": "0x9fc9c51f6ea3acb84184efa88ba4f02e7d161766",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "F2OzKsn6Wj...gtyORbyCQ==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x78ff9a7...647b6d62558c"
}
```
### reactionsByFid
Get all reactions by an FID
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| -------------- | ----------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------- |
| fid | The FID of the reaction's creator | `fid=6833` |
| reaction\_type | The type of reaction, use string representation | `reaction_type=Like` OR `reaction_type=Recast` |
| pageSize | Optional page size (default: 1000) | `pageSize=100` |
| pageToken | Optional page token for pagination | `pageToken=DAEDAAAGlQ...` |
| reverse | Optional reverse order flag | `reverse=true` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/reactionsByFid?fid=2&reaction_type=Like
```
**Response**
```json
{
"messages": [
{
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_REACTION_ADD",
"fid": 2,
"timestamp": 72752656,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"reactionBody": {
"type": "REACTION_TYPE_LIKE",
"targetCastId": {
"fid": 1795,
"hash": "0x7363f449bfb0e7f01c5a1cc0054768ed5146abc0"
}
}
},
"hash": "0x9fc9c51f6ea3acb84184efa88ba4f02e7d161766",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "F2OzKsn6WjP8MTw...hqUbrAvp6mggtyORbyCQ==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x78ff9a768...62558c"
}
],
"nextPageToken": ""
}
```
### reactionsByCast
Get all reactions to a cast
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| -------------- | ----------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------- |
| target\_fid | The FID of the cast's creator | `target_fid=6833` |
| target\_hash | The hash of the cast | `target_hash=0x7363f449bfb0e7f01c5a1cc0054768ed5146abc0` |
| reaction\_type | The type of reaction, use string representation | `reaction_type=Like` OR `reaction_type=Recast` |
| pageSize | Optional page size (default: 1000) | `pageSize=100` |
| pageToken | Optional page token for pagination | `pageToken=DAEDAAAGlQ...` |
| reverse | Optional reverse order flag | `reverse=true` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/reactionsByCast?target_fid=2&reaction_type=Like&target_hash=0x7363f449bfb0e7f01c5a1cc0054768ed5146abc0
```
**Response**
```json
{
"messages": [
{
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_REACTION_ADD",
"fid": 426,
"timestamp": 72750141,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"reactionBody": {
"type": "REACTION_TYPE_LIKE",
"targetCastId": {
"fid": 1795,
"hash": "0x7363f449bfb0e7f01c5a1cc0054768ed5146abc0"
}
}
},
"hash": "0x7662fba1be3166fc75acc0914a7b0e53468d5e7a",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "tmAUEYlt/+...R7IO3CA==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x13dd2...204e57bc2a"
}
],
"nextPageToken": ""
}
```
### reactionsByTarget
Get all reactions to cast's target URL
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| -------------- | ----------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| url | The URL of the parent cast | `url=chain://eip155:1/erc721:0x39d89b649ffa044383333d297e325d42d31329b2` |
| reaction\_type | The type of reaction, use string representation | `reaction_type=Like` OR `reaction_type=Recast` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/reactionsByTarget?url=chain://eip155:1/erc721:0x39d89b649ffa044383333d297e325d42d31329b2
```
**Response**
```json
{
"messages": [
{
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_REACTION_ADD",
"fid": 1134,
"timestamp": 79752856,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"reactionBody": {
"type": "REACTION_TYPE_LIKE",
"targetUrl": "chain://eip155:1/erc721:0x39d89b649ffa044383333d297e325d42d31329b2"
}
},
"hash": "0x94a0309cf11a07b95ace71c62837a8e61f17adfd",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "+f/+M...0Uqzd0Ag==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0xf6...3769198d4c"
}
],
"nextPageToken": ""
}
```
## Storage API
### storageLimitsByFid
Get an FID's storage limits.
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | ------------------------------ | ---------- |
| fid | The FID that's being requested | `fid=6833` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/storageLimitsByFid?fid=6833
```
**Response**
```json
{
"limits": [
{
"storeType": "Casts",
"name": "CASTS",
"limit": 77000,
"used": 10510,
"earliestTimestamp": 0,
"earliestHash": []
},
{
"storeType": "Links",
"name": "LINKS",
"limit": 38500,
"used": 1742,
"earliestTimestamp": 0,
"earliestHash": []
},
{
"storeType": "Reactions",
"name": "REACTIONS",
"limit": 38500,
"used": 19578,
"earliestTimestamp": 0,
"earliestHash": []
},
{
"storeType": "UserData",
"name": "USER_DATA",
"limit": 800,
"used": 8,
"earliestTimestamp": 0,
"earliestHash": []
},
{
"storeType": "Verifications",
"name": "VERIFICATIONS",
"limit": 400,
"used": 7,
"earliestTimestamp": 0,
"earliestHash": []
},
{
"storeType": "UsernameProofs",
"name": "USERNAME_PROOFS",
"limit": 80,
"used": 1,
"earliestTimestamp": 0,
"earliestHash": []
}
],
"units": 515,
"unit_details": [
{
"unitType": "UnitTypeLegacy",
"unitSize": 15
},
{
"unitType": "UnitType2024",
"unitSize": 1
},
{
"unitType": "UnitType2025",
"unitSize": 0
}
],
"tier_subscriptions": [
{
"tier_type": "Pro",
"expires_at": 1781630485
}
]
}
```
## UserData API
The UserData API will accept the following values for the `user_data_type` field.
| String | Numerical value | Description |
| -------------------------- | --------------- | ----------------------------- |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_PFP | 1 | Profile Picture for the user |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_DISPLAY | 2 | Display Name for the user |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_BIO | 3 | Bio for the user |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_URL | 5 | URL of the user |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_USERNAME | 6 | Preferred Name for the user |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_LOCATION | 7 | Location for the user |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_TWITTER | 8 | Twitter username for the user |
| USER\_DATA\_TYPE\_GITHUB | 9 | GitHub username for the user |
See [FIP-196](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/protocol/discussions/196) for more information on Location.
See [FIP-19](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/protocol/discussions/199) for more information on Twitter/X and Github usernames.
### userDataByFid
Get UserData for a FID.
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| ---------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- |
| fid | The FID that's being requested | `fid=6833` |
| user\_data\_type | The type of user data, either as a numerical value or type string. If this is omitted, all user data for the FID is returned | `user_data_type=1` OR `user_data_type=USER_DATA_TYPE_DISPLAY` |
| pageSize | Optional page size (default: 1000) | `pageSize=100` |
| pageToken | Optional page token for pagination | `pageToken=DAEDAAAGlQ...` |
| reverse | Optional reverse order flag | `reverse=true` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/userDataByFid?fid=6833&user_data_type=1
```
**Response**
```json
{
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_USER_DATA_ADD",
"fid": 6833,
"timestamp": 83433831,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"userDataBody": {
"type": "USER_DATA_TYPE_PFP",
"value": "https://i.imgur.com/HG54Hq6.png"
}
},
"hash": "0x327b8f47218c369ae01cc453cc23efc79f10181f",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "XITQZD7q...LdAlJ9Cg==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x0852...6e999cdd"
}
```
## Username Proofs API
### userNameProofByName
Get an proof for a username by the Farcaster username
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | ------------------------------------- | --------------------------------- |
| name | The Farcaster username or ENS address | `name=adityapk` OR `name=dwr.eth` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/userNameProofByName?name=adityapk
```
**Response**
```json
{
"timestamp": 1670603245,
"name": "adityapk",
"owner": "Oi7uUaECifDm+larm+rzl3qQhcM=",
"signature": "fo5OhBP/ud...3IoJdhs=",
"fid": 6833,
"type": "USERNAME_TYPE_FNAME"
}
```
### userNameProofsByFid
Get a list of proofs provided by an FID
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | ---------------------------------- | ------------------------- |
| fid | The FID being requested | `fid=2` |
| pageSize | Optional page size (default: 1000) | `pageSize=100` |
| pageToken | Optional page token for pagination | `pageToken=DAEDAAAGlQ...` |
| reverse | Optional reverse order flag | `reverse=true` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/userNameProofsByFid?fid=2
```
**Response**
```json
{
"proofs": [
{
"timestamp": 1623910393,
"name": "v",
"owner": "0x4114e33eb831858649ea3702e1c9a2db3f626446",
"signature": "bANBae+Ub...kr3Bik4xs=",
"fid": 2,
"type": "USERNAME_TYPE_FNAME"
},
{
"timestamp": 1690329118,
"name": "varunsrin.eth",
"owner": "0x182327170fc284caaa5b1bc3e3878233f529d741",
"signature": "zCEszPt...zqxTiFqVBs=",
"fid": 2,
"type": "USERNAME_TYPE_ENS_L1"
}
]
}
```
## Verifications API
### verificationsByFid
Get a list of verifications provided by an FID
**Query Parameters**
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| --------- | ------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------- |
| fid | The FID being requested | `fid=2` |
| address | The optional ETH address to filter by | `address=0x91031dcfdea024b4d51e775486111d2b2a715871` |
| pageSize | Optional page size (default: 1000) | `pageSize=100` |
| pageToken | Optional page token for pagination | `pageToken=DAEDAAAGlQ...` |
| reverse | Optional reverse order flag | `reverse=true` |
**Example**
```bash
curl http://127.0.0.1:3381/v1/verificationsByFid?fid=2
```
**Response**
```json
{
"messages": [
{
"data": {
"type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_VERIFICATION_ADD_ETH_ADDRESS",
"fid": 2,
"timestamp": 73244540,
"network": "FARCASTER_NETWORK_MAINNET",
"verificationAddEthAddressBody": {
"address": "0x91031dcfdea024b4d51e775486111d2b2a715871",
"ethSignature": "tyxj1...x1cYzhyxw=",
"blockHash": "0xd74860c4bbf574d5ad60f03a478a30f990e05ac723e138a5c860cdb3095f4296"
}
},
"hash": "0xa505331746ec8c5110a94bdb098cd964e43a8f2b",
"hashScheme": "HASH_SCHEME_BLAKE3",
"signature": "bln1zIZM.../4riB9IVBQ==",
"signatureScheme": "SIGNATURE_SCHEME_ED25519",
"signer": "0x78ff9...b6d62558c"
}
],
"nextPageToken": ""
}
```
## Blocks API
Used to retrieve blocks and shard chunks from the chain.
### API
| Method Name | Request Type | Response Type | Description |
| -------------- | ------------------ | ------------------- | -------------------------------------------- |
| GetBlocks | BlocksRequest | stream Block | Returns a stream of blocks for a given shard |
| GetShardChunks | ShardChunksRequest | ShardChunksResponse | Returns chunks of serialized block data |
### BlocksRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| -------------------- | ----------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------- |
| shard\_id | [uint32](#uint32) | | ID of the shard to get blocks from |
| start\_block\_number | [uint64](#uint64) | | Block number to start from (inclusive) |
| stop\_block\_number | [uint64](#uint64) | optional | Block number to stop at (inclusive) |
### ShardChunksRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| -------------------- | ----------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------- |
| shard\_id | [uint32](#uint32) | | ID of the shard to get chunks from |
| start\_block\_number | [uint64](#uint64) | | Block number to start from (inclusive) |
| stop\_block\_number | [uint64](#uint64) | optional | Block number to stop at (inclusive) |
### ShardChunksResponse
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------------- | --------------- | -------- | --------------------- |
| shard\_chunks | [ShardChunk](#) | repeated | Array of shard chunks |
### Block
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| -------- | ---------------- | -------- | ------------------------------ |
| header | [BlockHeader](#) | | Header info for the block |
| messages | [Message](#) | repeated | Array of messages in the block |
## Casts API
Used to retrieve valid casts or tombstones for deleted casts
### API
| Method Name | Request Type | Response Type | Description |
| ----------------------- | -------------------- | ---------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------- |
| GetCast | CastId | Message | Returns a specific Cast |
| GetCastsByFid | FidRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns CastAdds for an Fid in reverse chron order |
| GetCastsByParent | CastsByParentRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns CastAdd replies to a given Cast in reverse chron order |
| GetCastsByMention | FidRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns CastAdds that mention an Fid in reverse chron order |
| GetAllCastMessagesByFid | FidTimestampRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns Casts for an Fid with optional timestamp filtering |
### CastsByParentRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ---------------- | ----------------- | -------- | --------------------------------------------- |
| parent\_cast\_id | [CastId](#CastId) | | Parent cast ID to find replies for (optional) |
| parent\_url | [string](#string) | | Parent URL to find replies for (optional) |
| page\_size | [uint32](#uint32) | optional | Number of results to return per page |
| page\_token | [bytes](#bytes) | optional | Token for pagination |
| reverse | [bool](#bool) | optional | Whether to return results in reverse order |
### FidTimestampRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ---------------- | ----------------- | -------- | ------------------------------------------ |
| fid | [uint64](#uint64) | | Farcaster ID |
| page\_size | [uint32](#uint32) | optional | Number of results to return per page |
| page\_token | [bytes](#bytes) | optional | Token for pagination |
| reverse | [bool](#bool) | optional | Whether to return results in reverse order |
| start\_timestamp | [uint64](#uint64) | optional | Optional timestamp to start filtering from |
| stop\_timestamp | [uint64](#uint64) | optional | Optional timestamp to stop filtering at |
## Events API
Used to subscribe to real-time event updates from the Snapchain node
### API
| Method Name | Request Type | Response Type | Description |
| ----------- | ---------------- | --------------- | ---------------------------------- |
| Subscribe | SubscribeRequest | stream HubEvent | Streams new Events as they occur |
| GetEvent | EventRequest | HubEvent | Returns a single event by ID |
| GetEvents | EventsRequest | EventsResponse | Returns a paginated list of events |
### SubscribeRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------------ | ----------------- | -------- | -------------------------------- |
| event\_types | [HubEventType](#) | repeated | Types of events to subscribe to |
| from\_id | uint64 | optional | Event ID to start streaming from |
| shard\_index | uint32 | optional | Shard index to subscribe to |
### EventRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------------ | ----------- | ----- | ------------------------- |
| id | [uint64](#) | | Event ID to retrieve |
| shard\_index | [uint32](#) | | Shard index for the event |
### EventsRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------------ | ----------- | -------- | ----------------------------------------- |
| start\_id | [uint64](#) | | Starting event ID |
| shard\_index | [uint32](#) | optional | Shard index to query |
| stop\_id | [uint64](#) | optional | Stopping event ID |
| page\_size | [uint32](#) | optional | Number of events to return per page |
| page\_token | [bytes](#) | optional | Page token for pagination |
| reverse | [bool](#) | optional | Whether to return events in reverse order |
### EventsResponse
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------------- | ------------- | -------- | ------------------------------ |
| events | [HubEvent](#) | repeated | List of events |
| next\_page\_token | [bytes](#) | optional | Token for next page of results |
## Fids API
Used to retrieve a list of all fids
### API
| Method Name | Request Type | Response Type | Description |
| ----------- | ------------ | ------------- | ------------------------------------ |
| GetFids | FidsRequest | FidsResponse | Returns a paginated list of all fids |
### FidsRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------- | ----------------- | -------- | ----------- |
| page\_size | [uint32](#uint32) | optional | |
| page\_token | [bytes](#bytes) | optional | |
| reverse | [bool](#bool) | optional | |
| shard\_id | [uint32](#uint32) | required | |
### Fids Response
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------------- | --------------- | -------- | ------------- |
| fids | [uint64](#) | repeated | Array of fids |
| next\_page\_token | [bytes](#bytes) | optional | |
## GRPC API
Snapchain nodes serve a gRPC API on port 3383 by default.
### Using the API
We recommend using a library
like [hub-nodejs](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/hub-monorepo/tree/main/packages/hub-nodejs) to interact with the
gRPC APIs. Please refer
to its [documentation](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/hub-monorepo/tree/main/packages/hub-nodejs/docs) for how to use
it.
### Other languages
The protobufs for the gRPC API are available within
the [hub-monorepo](https://github.com/farcasterxyz/hub-monorepo/tree/main/protobufs). They can be used to generate
bindings for other clients built using other languages. Note that by default, nodes rely on the
javascript [ts-proto](https://www.npmjs.com/package/ts-proto) library's serialization byte order to verify messages
hashes. If you are using a different client, you may need to use the `data_bytes` field with the raw serialized bytes
when calling `SubmitMessage` in order for the message to be considered valid. Refer to
the [SubmitMessage HTTP API docs](/reference/httpapi/message#using-with-rust-go-or-other-programing-languages)
for more details.
## Links API
A Link represents a relationship between two users (e.g. follow)
### API
| Method Name | Request Type | Response Type | Description |
| ------------------------------- | -------------------- | ---------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------- |
| GetLink | LinkRequest | Message | Returns a specific Link |
| GetLinksByFid | LinksByFidRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns Links made by an fid in reverse chron order |
| GetLinksByTarget | LinksByTargetRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns LinkAdds for a given target in reverse chron order |
| GetLinkCompactStateMessageByFid | FidRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns compact state messages for Links by an fid |
| GetAllLinkMessagesByFid | FidTimestampRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns Links made by an fid with optional timestamp filtering |
### Link Request
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------- | ----------- | ----- | ----------------------------------------------- |
| fid | [uint64](#) | | Farcaster ID of the user who generated the Link |
| link\_type | [string](#) | | Type of the Link being requested |
| target\_fid | [uint64](#) | | Fid of the target |
### LinksByFid Request
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------- | ----------- | -------- | ----------------------------------------------- |
| fid | [uint64](#) | | Farcaster ID of the user who generated the Link |
| link\_type | string | optional | Type of the Link being requested |
| page\_size | uint32 | optional | Number of results to return per page |
| page\_token | bytes | optional | Token for pagination |
| reverse | boolean | optional | Whether to return results in reverse order |
### LinksByTarget Request
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------- | ----------- | -------- | ------------------------------------------ |
| target\_fid | [uint64](#) | | Target Farcaster ID to find links for |
| link\_type | string | optional | Type of the Link being requested |
| page\_size | uint32 | optional | Number of results to return per page |
| page\_token | bytes | optional | Token for pagination |
| reverse | boolean | optional | Whether to return results in reverse order |
### FidTimestampRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ---------------- | ----------------- | -------- | ------------------------------------------ |
| fid | [uint64](#uint64) | | Farcaster ID |
| page\_size | [uint32](#uint32) | optional | Number of results to return per page |
| page\_token | [bytes](#bytes) | optional | Token for pagination |
| reverse | [bool](#bool) | optional | Whether to return results in reverse order |
| start\_timestamp | [uint64](#uint64) | optional | Optional timestamp to start filtering from |
| stop\_timestamp | [uint64](#uint64) | optional | Optional timestamp to stop filtering at |
## Message API
Used to validate and send a message to the Snapchain node. Valid messages are accepted and gossiped to other nodes in the
network.
### API
| Method Name | Request Type | Response Type | Description |
| ------------------ | ------------------------- | -------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- |
| SubmitMessage | Message | Message | Submits a Message to the node |
| SubmitBulkMessages | SubmitBulkMessagesRequest | SubmitBulkMessagesResponse | Submits several Messages to the node |
| ValidateMessage | Message | ValidationResponse | Validates a Message on the node without merging and gossiping |
### SubmitBulkMessagesRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| -------- | ------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| messages | Message | repeated | An array of Messages to submit. All messages will submitted, even if earlier ones fail |
### SubmitBulkMessagesResponse
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| -------- | ------------------- | -------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| messages | BulkMessageResponse | repeated | An array of BulkMessageResponse, one for each submitted message indicating success or failure |
### BulkMessageResponse
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| -------------- | ------------ | ----- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
| message | Message | oneOf | The message if it was submitted successfully |
| message\_error | MessageError | oneOf | Failure reason if the message was not submitted successfully |
## MessageError
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------- | ------ | ----- | --------------------------------- |
| hash | bytes | | Message hash |
| errCode | string | | Failure error code |
| message | string | | Description of the failure reason |
### ValidationResponse
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------- | ------- | ----- | --------------------------------------------- |
| valid | boolean | | Whether the message is valid or not |
| message | Message | | The message being validated (same as request) |
## Metadata API
These APIs are used to retrieve node metadata and for synchronization between nodes. Some methods are not meant for use by external applications.
### API
| Method Name | Request Type | Response Type | Description |
| ----------------------- | ----------------------- | ------------------------ | ----------------------------------------- |
| GetInfo | GetInfoRequest | GetInfoResponse | Returns metadata about the node's state |
| GetTrieMetadataByPrefix | TrieNodeMetadataRequest | TrieNodeMetadataResponse | Get trie metadata for a particular prefix |
### GetInfoRequest
Empty request, no parameters needed.
### GetInfoResponse
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------------ | ------------------- | -------- | ---------------------------- |
| db\_stats | [DbStats](#DbStats) | | Database statistics |
| num\_shards | [uint32](#uint32) | | Number of shards in the node |
| shard\_infos | [ShardInfo](#) | repeated | Information about each shard |
### DbStats
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------------------- | ----------------- | ----- | ----------------------------------------- |
| num\_messages | [uint64](#uint64) | | Total number of messages in the node |
| num\_fid\_registrations | [uint64](#uint64) | | Number of FID registrations in the node |
| approx\_size | [uint64](#uint64) | | Approximate size of the database in bytes |
### ShardInfo
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------------------- | ----------------- | ----- | ---------------------------------------- |
| shard\_id | [uint32](#uint32) | | Shard identifier |
| max\_height | [uint64](#uint64) | | Maximum block height in the shard |
| num\_messages | [uint64](#uint64) | | Number of messages in the shard |
| num\_fid\_registrations | [uint64](#uint64) | | Number of FID registrations in the shard |
| approx\_size | [uint64](#uint64) | | Approximate size of the shard in bytes |
| block\_delay | [uint64](#uint64) | | Block delay in the shard |
| mempool\_size | [uint64](#uint64) | | Size of the mempool for this shard |
### TrieNodeMetadataRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| --------- | ----------------- | ----- | ---------------------------- |
| shard\_id | [uint32](#uint32) | | Shard ID to get metadata for |
| prefix | [bytes](#bytes) | | Prefix to get metadata for |
### TrieNodeMetadataResponse
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------------- | ----------------------------------------------------- | -------- | ------------------------------------ |
| prefix | [bytes](#bytes) | | Prefix of the trie node |
| num\_messages | [uint64](#uint64) | | Number of messages under this prefix |
| hash | [string](#string) | | Hash of the trie node |
| children | [TrieNodeMetadataResponse](#TrieNodeMetadataResponse) | repeated | Child nodes of this trie node |
## OnChainEvents API
Used to retrieve on chain events (id registry, keys, storage rent)
### API
| Method Name | Request Type | Response Type | Description |
| ---------------------------------- | ------------------------------- | ---------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| GetOnChainSigner | SignerRequest | OnChainEvent | Returns the onchain event for an active signer for an Fid |
| GetOnChainSignersByFid | FidRequest | OnChainEventResponse | Returns all active account keys (signers) add events for an Fid |
| GetIdRegistryOnChainEvent | FidRequest | OnChainEvent | Returns the most recent register/transfer on chain event for an fid |
| GetIdRegistryOnChainEventByAddress | IdRegistryEventByAddressRequest | OnChainEvent | Returns the registration/transfer event by address if it exists (allows looking up fid by address) |
| GetOnChainEvents | OnChainEventRequest | OnChainEventResponse | Returns all on chain events filtered by type for an Fid (includes inactive keys and expired rent events) |
| GetFidAddressType | FidAddressTypeRequest | FidAddressTypeResponse | Returns address type information for a given fid and address |
### Signer Request
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------ | ----------- | ----- | ------------------------------------------------- |
| fid | [uint64](#) | | Farcaster ID of the user who generated the Signer |
| signer | [bytes](#) | | Public Key of the Signer |
### Fid Request
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------- | ----------- | ----- | ------------------------------------------- |
| fid | [uint64](#) | | Farcaster ID of the user |
| page\_size | uint32 | | (optional) Type of the Link being requested |
| page\_token | bytes | | (optional)Type of the Link being requested |
| reverse | boolean | | (optional) Ordering of the response |
##### IdRegistryEventByAddressRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------- | --------------- | ----- | ----------- |
| address | [bytes](#bytes) | | |
##### OnChainEventResponse
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------------- | ----------------------------- | -------- | ----------- |
| events | [OnChainEvent](#onchainevent) | repeated | |
| next\_page\_token | [bytes](#bytes) | optional | |
##### FidAddressTypeRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------- | --------------- | ----- | ---------------- |
| fid | [uint64](#) | | Farcaster ID |
| address | [bytes](#bytes) | | Address to check |
##### FidAddressTypeResponse
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------------ | --------- | ----- | ---------------------------------------- |
| is\_custody | [bool](#) | | Whether the address is a custody address |
| is\_auth | [bool](#) | | Whether the address is an auth address |
| is\_verified | [bool](#) | | Whether the address is verified |
## Reactions API
### API
| Method Name | Request Type | Response Type | Description |
| --------------------------- | ------------------------ | ---------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| GetReaction | ReactionRequest | Message | Returns a specific Reaction |
| GetReactionsByFid | ReactionsByFidRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns Reactions made by an Fid in reverse chron order |
| GetReactionsByCast | ReactionsByTargetRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns ReactionAdds for a given Cast in reverse chron order (To be deprecated) |
| GetReactionsByTarget | ReactionsByTargetRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns ReactionAdds for a given target (cast or URL) in reverse chron order |
| GetAllReactionMessagesByFid | FidTimestampRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns Reactions made by an Fid with optional timestamp filtering |
### Reaction Request
Used to retrieve valid or revoked reactions
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ---------------- | ----------------- | ----- | --------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| fid | [uint64](#) | | Farcaster ID of the user who generated the Reaction |
| reaction\_type | [ReactionType](#) | | Type of the Reaction being requested |
| target\_cast\_id | [CastId](#) | | (optional) Identifier of the Cast whose reactions are being requested |
| target\_url | [string](#) | | (optional) Identifier of the Url whose reactions are being requested |
### ReactionsByFid Request
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| -------------- | ----------------- | -------- | --------------------------------------------------- |
| fid | [uint64](#) | | Farcaster ID of the user who generated the Reaction |
| reaction\_type | [ReactionType](#) | optional | Type of the Reaction being requested |
| page\_size | uint32 | optional | Number of results to return per page |
| page\_token | bytes | optional | Token for pagination |
| reverse | boolean | optional | Whether to return results in reverse order |
### ReactionsByTargetRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ---------------- | ----------------------------- | -------- | ----------------------------------------------- |
| target\_cast\_id | [CastId](#CastId) | | Target cast ID to find reactions for (optional) |
| target\_url | [string](#string) | | Target URL to find reactions for (optional) |
| reaction\_type | [ReactionType](#ReactionType) | optional | Type of reaction to filter by |
| page\_size | [uint32](#uint32) | optional | Number of results to return per page |
| page\_token | [bytes](#bytes) | optional | Token for pagination |
| reverse | [bool](#bool) | optional | Whether to return results in reverse order |
### FidTimestampRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ---------------- | ----------------- | -------- | ------------------------------------------ |
| fid | [uint64](#uint64) | | Farcaster ID |
| page\_size | [uint32](#uint32) | optional | Number of results to return per page |
| page\_token | [bytes](#bytes) | optional | Token for pagination |
| reverse | [bool](#bool) | optional | Whether to return results in reverse order |
| start\_timestamp | [uint64](#uint64) | optional | Optional timestamp to start filtering from |
| stop\_timestamp | [uint64](#uint64) | optional | Optional timestamp to stop filtering at |
## Storage API
Get an FID's storage limits.
### API
| Method Name | Request Type | Response Type | Description |
| ---------------------------- | ------------ | --------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------- |
| GetCurrentStorageLimitsByFid | FidRequest | StorageLimitsResponse | Returns current storage limits for all stores for an Fid |
##### StorageLimitsResponse
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------------------- | ----------------------- | -------- | ----------------------------- |
| limits | [StorageLimit](#) | repeated | Storage limits per store type |
| units | [uint32](#) | | Number of units |
| unit\_details | [StorageUnitDetails](#) | repeated | Details about storage units |
| tier\_subscriptions | [TierDetails](#) | repeated | Tier subscription details |
##### StorageLimit
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------------- | -------------- | ----- | ------------------------------------------------------ |
| store\_type | [StoreType](#) | | The specific type being managed by the store |
| name | [string](#) | | Name of the store type |
| limit | [uint64](#) | | The limit of the store type, scaled by the user's rent |
| used | [uint64](#) | | Current usage of the store type |
| earliestTimestamp | [uint64](#) | | Timestamp of earliest message |
| earliestHash | [bytes](#) | | Hash of earliest message |
##### StorageUnitDetails
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ---------- | -------------------- | ----- | ------------------------ |
| unit\_type | [StorageUnitType](#) | | Type of storage unit |
| unit\_size | [uint32](#) | | Size of the storage unit |
##### TierDetails
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------- | ------------- | ----- | -------------------- |
| tier\_type | [TierType](#) | | Type of tier |
| expires\_at | [uint64](#) | | Expiration timestamp |
## UserData API
Used to retrieve the current metadata associated with a user
### API
| Method Name | Request Type | Response Type | Description |
| --------------------------- | ------------------- | ---------------- | -------------------------------------------------------- |
| GetUserData | UserDataRequest | Message | Returns a specific UserData for an Fid |
| GetUserDataByFid | FidRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns all UserData for an Fid |
| GetAllUserDataMessagesByFid | FidTimestampRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns all UserData for an Fid with timestamp filtering |
### UserData Request
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ---------------- | ----------------- | ----- | --------------------------------------------------- |
| fid | [uint64](#) | | Farcaster ID of the user who generated the UserData |
| user\_data\_type | [UserDataType](#) | | Type of UserData being requested |
### Messages Response
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----------------- | --------------- | -------- | ----------------------- |
| messages | [Message](#) | repeated | Farcaster Message array |
| next\_page\_token | [bytes](#bytes) | optional | Token for pagination |
### FidTimestampRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ---------------- | ----------------- | -------- | ------------------------------------------ |
| fid | [uint64](#uint64) | | Farcaster ID |
| page\_size | [uint32](#uint32) | optional | Number of results to return per page |
| page\_token | [bytes](#bytes) | optional | Token for pagination |
| reverse | [bool](#bool) | optional | Whether to return results in reverse order |
| start\_timestamp | [uint64](#uint64) | optional | Optional timestamp to start filtering from |
| stop\_timestamp | [uint64](#uint64) | optional | Optional timestamp to stop filtering at |
## Username Proofs API
Used to retrieve proofs of username ownership.
### API
| Method Name | Request Type | Response Type | Description |
| ---------------------- | --------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------- |
| GetUsernameProof | [UsernameProofRequest](#UsernameProofRequest) | [UserNameProof](#UserNameProof) | Gets username proof by name |
| GetUserNameProofsByFid | [FidRequest](#FidRequest) | [UsernameProofsResponse](#UsernameProofsResponse) | Gets all username proofs for an FID |
### UsernameProofRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ----- | --------------- | ----- | ------------------------- |
| name | [bytes](#bytes) | | Username to get proof for |
### UsernameProofsResponse
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------ | ------------------------------- | -------- | ------------------------ |
| proofs | [UserNameProof](#UserNameProof) | repeated | Array of username proofs |
### UserNameProof
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| --------- | ----------------------------- | ----- | -------------------------------------- |
| timestamp | [uint64](#uint64) | | Timestamp of the proof |
| name | [bytes](#bytes) | | Username being proved |
| owner | [bytes](#bytes) | | Owner address |
| signature | [bytes](#bytes) | | Cryptographic signature |
| fid | [uint64](#uint64) | | Farcaster ID associated with the proof |
| type | [UserNameType](#UserNameType) | | Type of username proof |
## Verifications API
Used to retrieve valid or revoked proof of ownership of an Ethereum Address.
### API
| Method Name | Request Type | Response Type | Description |
| ------------------------------- | ------------------- | ---------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
| GetVerification | VerificationRequest | Message | Returns a VerificationAdd for an Ethereum Address |
| GetVerificationsByFid | FidRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns all VerificationAdds made by an Fid |
| GetAllVerificationMessagesByFid | FidTimestampRequest | MessagesResponse | Returns all Verifications made by an Fid with time filtering |
### Verification Request
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ------- | ----------- | ----- | ------------------------------------------------------- |
| fid | [uint64](#) | | Farcaster ID of the user who generated the Verification |
| address | [bytes](#) | | Ethereum Address being verified |
### FidTimestampRequest
| Field | Type | Label | Description |
| ---------------- | ----------------- | -------- | ------------------------------------------ |
| fid | [uint64](#uint64) | | Farcaster ID |
| page\_size | [uint32](#uint32) | optional | Number of results to return per page |
| page\_token | [bytes](#bytes) | optional | Token for pagination |
| reverse | [bool](#bool) | optional | Whether to return results in reverse order |
| start\_timestamp | [uint64](#uint64) | optional | Optional timestamp to start filtering from |
| stop\_timestamp | [uint64](#uint64) | optional | Optional timestamp to stop filtering at |